The 5G future is here. Years in the making, the long-buzzed-about fifth generation of wireless connectivity has become a reality, ushering in an era of radical new possibilities in many industries.
Innovative use cases such as autonomous drones and smart city ecosystems promise increased efficiency and productivity for governments and businesses in a post-pandemic world, and pervasive benefits across the globe, says PwC Report “The global economic impact of 5G“.
5G will be a key part of companies’ new operating environment and technology toolkit, but to realise the technology’s potential productivity and efficiency gains they’ll need a strategic approach.
5G for business
For business, 5G is about more than just mobile speeds. New levels of connection will amplify the insight leaders get from connected technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and the internet of things (IoT). Powered by 5G, PwC believes businesses will be able to see, do and achieve more.
New use cases and business models will almost certainly emerge from this era of hyperconnection. Organisations that are prepared for 5G will likely see improved operations and differentiating customer experiences as they leverage 5G’s speed and reliability.
The promise of 5G adoption
The promise of 5G has been echoed throughout the business world for years. 5G’s faster speed, lower latency and ability to connect vastly higher numbers of devices than previous generations of mobile technology offered executives a glimpse of a more efficient and productive future. By providing the basis for ubiquitous ultra-fast broadband, 5G opens up possibilities far beyond the reach of 4G or Wi-Fi 6. This promise has only grown more critical today, as leaders consider how best to repair, rethink and reconfigure their business for the post–COVID-19 world.
As 5G’s adoption and rollout accelerate, we can begin to quantify the technology’s potential impact in economic terms. Drawing on expert insight and using economic modelling, we started at the use-case level to assess what that impact will be.
5G focused on five industries
We focused on five industries—healthcare, smart utilities, consumer and media, industrial manufacturing, and financial services—that stand to benefit significantly from 5G technology and calculated what that benefit could look like through 2030.
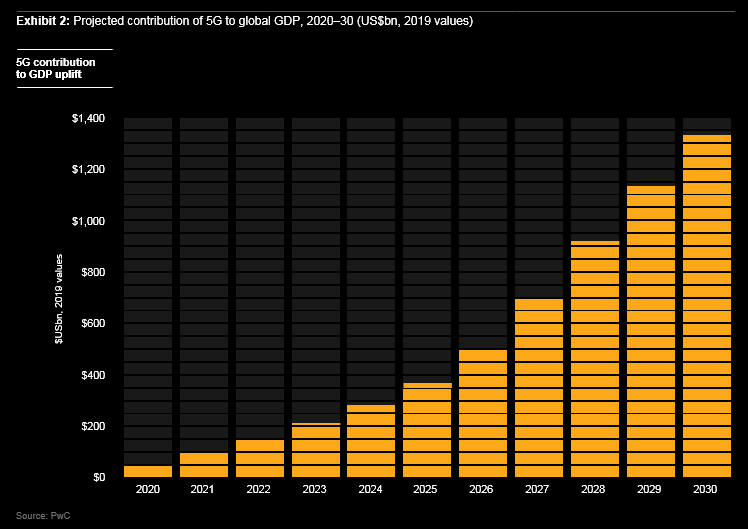
As with any such analysis, the absolute figures can only be directional and are most interesting when looked at in relation to one another. More than 80% of the economic potential appears to lie in healthcare applications (projected to contribute US$530bn to global GDP), smart utilities management (an additional US$330bn), and consumer and media applications (US$254bn more).
Smaller contributions from the other industries in our study bring the total estimated uplift to US$1.3tn. As leaders contemplate the decade ahead, 5G demands strategic attention—both to where and how it can create competitive advantages, and to the implementation and integration imperatives that must be met for it to generate value.
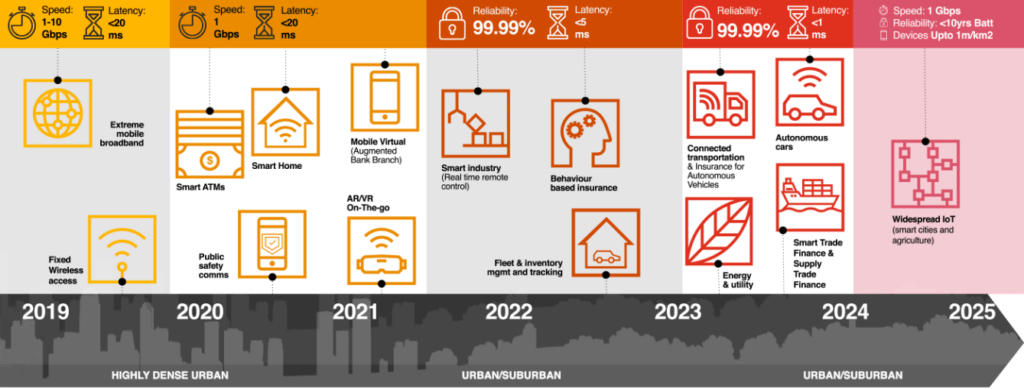
5G—the next generation of mobile connectivity
As 5G—the next generation of mobile connectivity—rolls out in coming years, it will create value in many industries and for society as a whole. Innovative uses of the technology show promise in a wide variety of settings: hospitals equipped with 5G devices that enable remote patient monitoring, and smart ambulances that communicate with doctors in real time; digital wallets that connect phones, wearables, cars and other devices to create seamless financial transactions; and 5G-enabled factories in which connections can be maintained among more sensors than ever before.
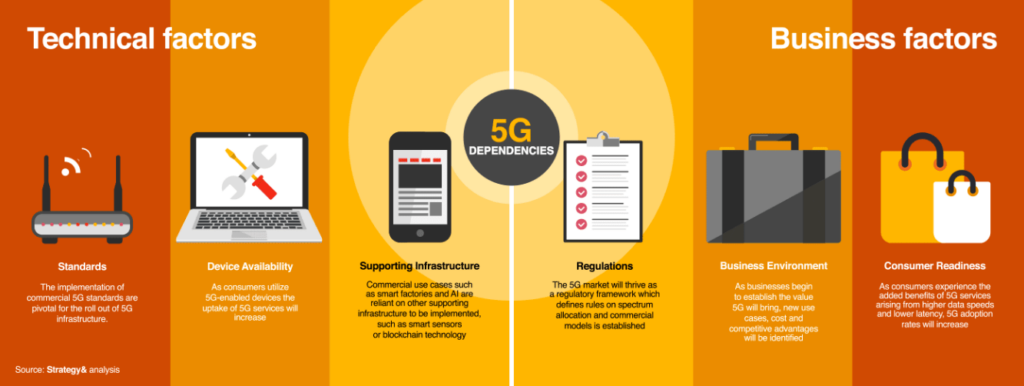
Mastering the 5G takeoff requires careful timing. Six key business and technical factors influence 5G readiness:
The size and nature of 5G’s economic impact will vary by industry and country. In healthcare, for example, in a single-payer, taxation-funded system, the effect may be to free up government resources to spend on other programmes and possibly lower taxes. In a private insurance–based system, the efficiencies of 5G could enable consumers to reallocate spending to other sectors.
5G enables a vast wave of innovative solutions and use cases
When these effects are added together, the potential impact is huge. Healthcare will be far and away the biggest contributor to the economic gains from 5G: our model predicts that it could add more than half a trillion dollars to global GDP.
But other industries also show significant potential, as 5G enables a vast wave of innovative solutions and use cases. In this study, we analysed use cases, both new and established, in five sectors—healthcare, smart utilities, consumer and media, industrial manufacturing, and financial services—and found that, in aggregate, the adoption of 5G will add US$1.3tn to global GDP by 2030.

These numbers quantify impact, but perhaps more important, our study findings reflect the value of 5G. The new levels of connectivity and collaboration that 5G enables will amplify and deepen the insight that organisations can gain from connected technologies. Companies will be able to see, attempt and achieve more, opening up new opportunities for growth as they rethink and reconfigure the way they do business in the post-pandemic world.
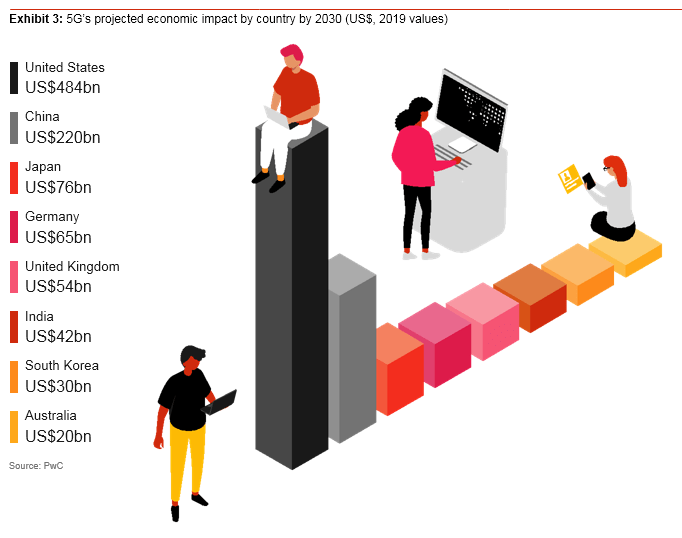
At the regional level, North America will experience the biggest percentage uplift to GDP from 5G, followed by Asia and Oceania and then by Europe, the Middle East and Africa (EMEA). In absolute dollar terms, North America also will rank highest, and Asia and Oceania is projected to outpace EMEA because of its larger overall economy.
Among the countries analysed, those with strong, modern industrial production sectors may benefit more than those that rely on service industries such as banking.
5G can enable cost savings and better health outcomes
The rapid rise of telemedicine during the COVID-19 pandemic provides a glimpse of the future of healthcare, but remote care is just one area in which 5G can enable both cost savings and better health outcomes.
For example, 5G will improve efficiency and productivity in hospitals through advances such as 5G-enabled tracking of medical devices and patient beds and the application of AI to 5G sensor data to trigger actions automatically and accelerate patient handovers.
We believe that the rising use of 5G—boosted by advances in robotics, IoT and AI—will enable the emergence of a new, connected healthcare ecosystem aligned with the concept of ‘4P’ medicine: predictive, preventative, personalised and participatory.
This ecosystem will use 5G connectivity to meet patient and provider needs accurately, conveniently, cost-effectively and at a massive scale.









Comments are closed.