The insurance industry has generally been a laggard when it comes to digital transformation. Yet a new class of venture-backed insurtech startups is beginning to disrupt incumbents by exploiting the weaknesses of the traditional insurance ecosystem. Beinsure Media has collected the opinions of insurtech experts and PitchBook`s data analytics adn presents a InsurTech`s evolution and investment review.
InsurTech Startups are developing new approaches

So far, emerging providers have largely just nibbled around the edges of the industry, but their success in penetrating new markets (such as cyber risk) and attracting underserved customers (such as gig economy workers) increasingly threatens incumbents who have been slow to respond.
InsurTech Startups are developing new approaches to traditional activities, such as underwriting and claims management, that could give them an edge.
As traditional competitors seek to maintain market share, they are focusing on providing targeted products, improving customer onboarding processes and deepening their relationships with existing customers.
These initiatives tend to take the form of investments, partnerships, and acquisitions. While these approaches may help improve incumbents’ competitive posture, they also drive opportunities for startups to help legacy providers fill the gaps in their offerings.
InsurTech category

The pandemic may accelerate these technology-based initiatives as those gaps — such as in-person insurance sales or claims adjustments — become more evident.
PitchBook data regarding the insurtech category underscores how large the startup niche has grown. Per the data company, $20 billion was spent last year on insurtech startups across venture capital, private equity and M&A activity.
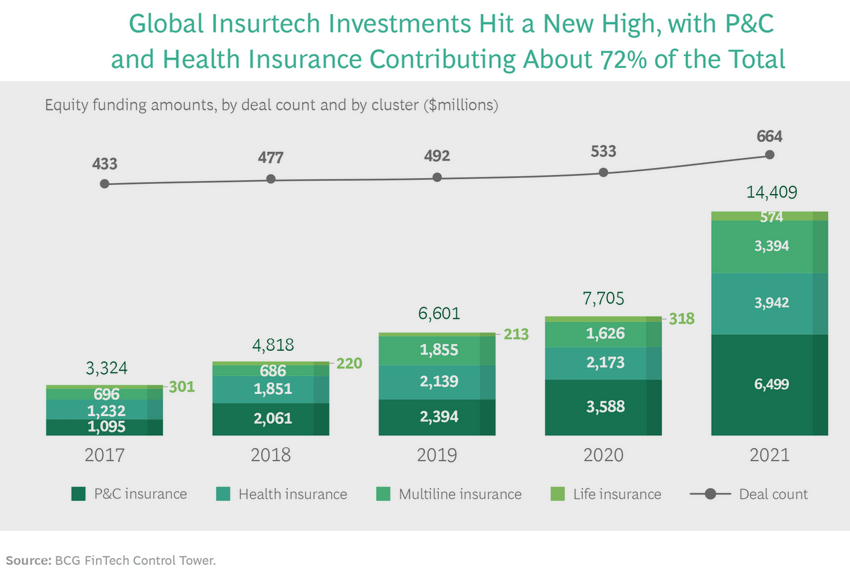
Private capital continued to flood the insurance industry, driving total investments in insurtechs to new heights across all insurance types, investment stages, and regions.
To meet the demands of customers seeking smarter and more efficient products and services — and to compete more effectively with insurtechs — many insurance incumbents are fast-tracking next-generation “bionic” operating models that combine the best of human and technological capabilities. The digital transformation of the industry appears to be in high gear.
TechCrunch divides insurtech startups into three categories:
- neoinsurance providers
- insurtech marketplaces
- insurtech enablers
Briefly, neoinsurance providers are companies like Root, Metromile and Next Insurance, which use technology to underwrite and sell insurance in an updated manner; these companies also often have optimized mobile experiences.
Marketplaces like The Zebra, Gabi, Insurify and others provide a way for consumers to better identify their insurance options. And, finally, there are companies like AgentSync, which fit neatly into our third category of firms that help other companies in the insurance business digitize their operations or otherwise modernize.
Since the end of the first quarter, we’ve seen several players in the broad startup category announce new capital, including Clearcover, Alan, Next Insurance and The Zebra.
But the sector is enough of a mixed bag that one needs to segment down to get clarity on how constituent companies are performing. So while Clearcover’s $200 million round from last week, Next Insurance’s $250 million round from the first of the month and Alan’s $220 million round from yesterday are interesting, this morning we’re going to focus a bit more on The Zebra’s side of the insurtech house. Insurtech marketplaces came back into our view when The Zebra put together a $150 million Series D and released a host of metrics regarding its growth.
Insurance remains a critical market within the global economy. The industry’s total direct written premiums (DWP) reached $7 trillion in 2023, or 7.2% of global GDP.
Investors have been making significant bets in the industry in recent years. In 2022, cumulative global deal value across VC, PE, and M&A for insurtech companies reached $20 billion, which was slightly lower than 2020`s $18.3 billion and 2019’s $19.3 billion in deals.
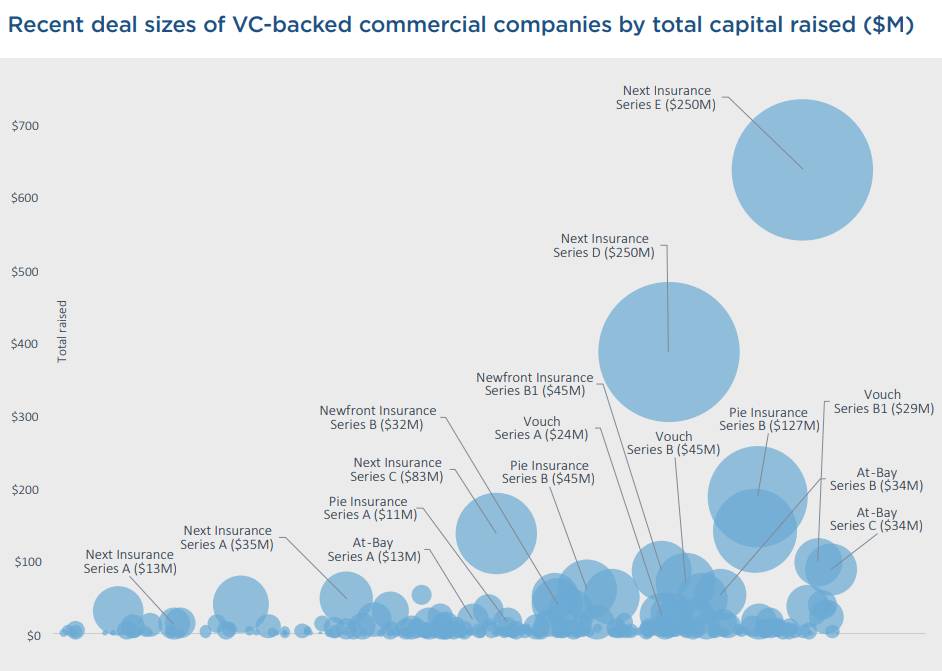
The lackluster market performance of newly minted public companies did not put a dent in private investment.
Insurtech Investment
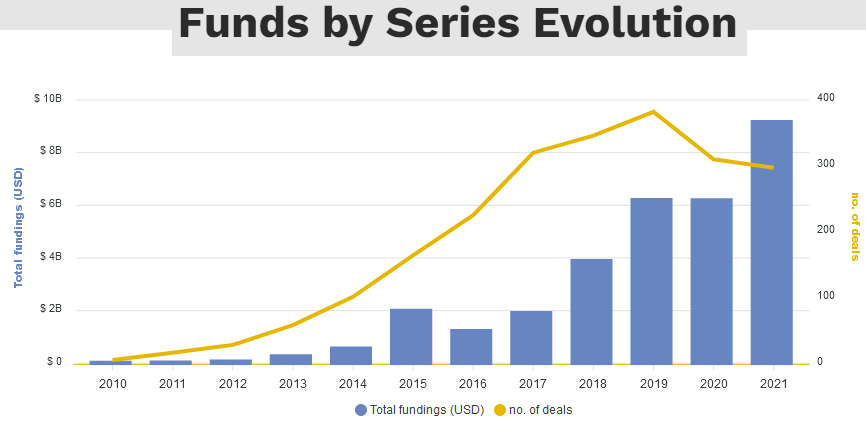
Insurtechs raised $14.4 billion across 644 deals in 2023, surpassing the total raised in 2021 by about 87% and reaching a cumulative ten-year total of $43.8 billion from 2012 to 2023. To put that in perspective, it took them seven years (from 2012 to 2018) to raise $15 billion.
Megarounds exceeding $100 million remain a key growth driver, as approximately half of the capital invested went to 37 companies.
Still, we believe the disruption opportunity remains significant and attribute this pullback primarily to the pandemic. M&A remains the core driver of investments with more than $10 billion invested.
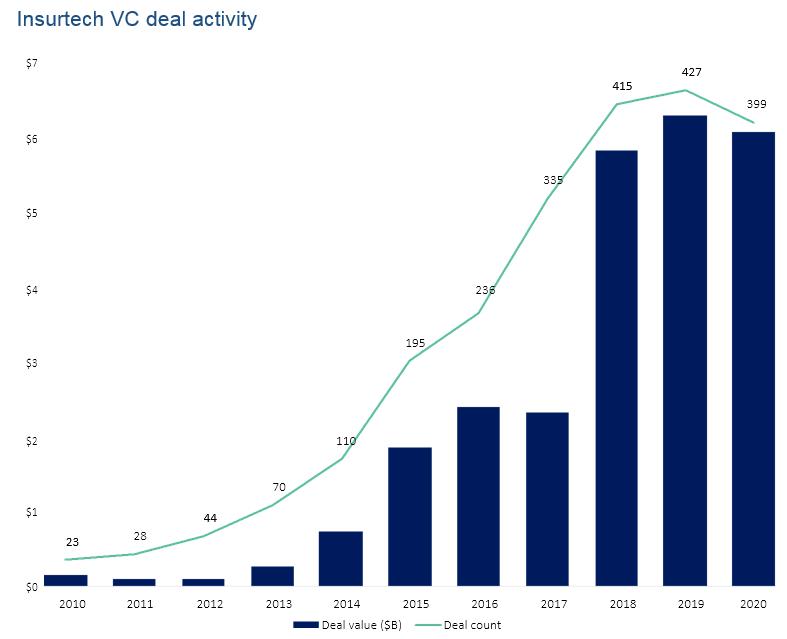
2021 was without a doubt a prosperous year for Insurtechs, with global investments reaching $10B. This represents an increase of 38% when compared to 2023. We can observe a boom in the Insurtech market with a new historical rise and a solid consolidation of the market.
Last year has shown a much more diverse landscape in terms of the regions where funding has grown. Growth has occurred in three main areas: Asia, Europe and the United States, said NTT Data.
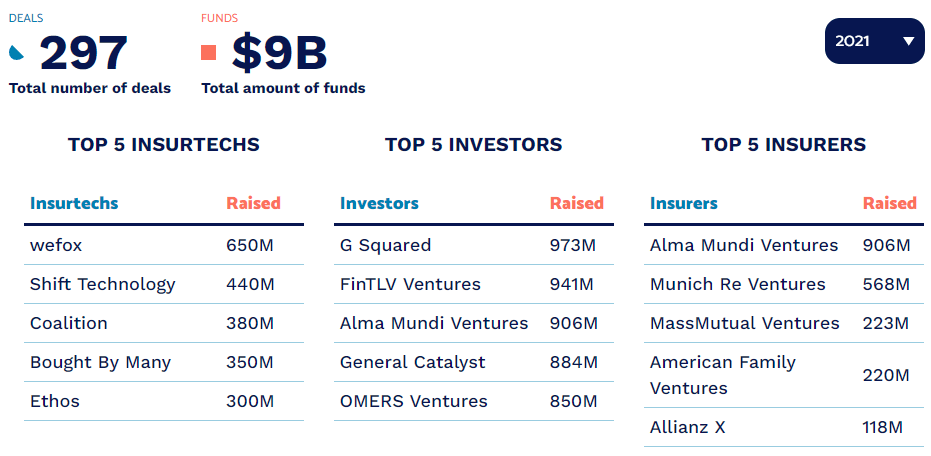
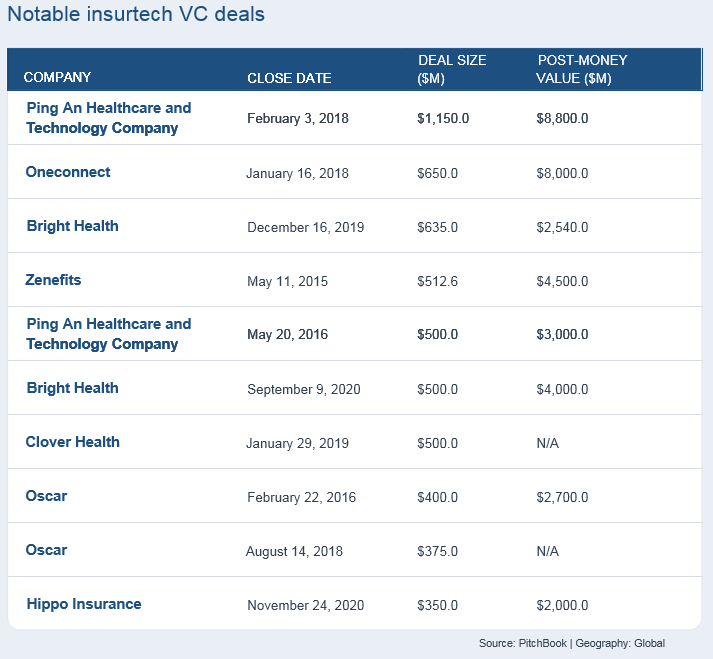
Notable Insurtech VC deals
Incorporating alternative datasets into underwriting science
Reinsurance underwriting hashistorically been an expensive, highly manual, and inefficient process that suffers from data errors and omissions. These challenges have created long-standing industry premium leakage—inadequate information leading to mispriced premiums. Several startups are seeking to apply AI & ML to insurance customer data improve underwriting decisions.
Cytora’s “programmable insurance” platform enables commercial insurers to integrate more data into the underwriting process to improve risk selection and refine policy pricing. The company utilizes reverse geocoding for address accuracy and to identify adjacent occupancies to enhance commercial property underwriting.
Cape Analytics provides property intelligence using a database of more than 70 million residential and commercial buildings in the US. The platform incorporates computer vision, geospatial imaging, and deep learning to identify property attributes that could have an impact on risk profiles, such as roof conditions (i.e. missing shingles, discoloration), distance to dry vegetation, nearby fuel loads, or other risk factors.
Insurtech Funds
Policy analysis and review
Assessing the consistency of policy language and coverageterms across an insurance portfolio is complicated, error prone, and time consuming, creating an opportunity for startups to automate the process. The inability for insurers to properly make these assessments could lead to productivity churn and increased business cyber risk.
RiskGenius utilizes natural language processing (NLP) and other data technologies to improve coverage accuracy and reduce review times for commercial insurers. Its SaaS platform allows customers to significantly speed up the process of checking policies for errors and omissions, benchmarking for compliance with internal standards and improving the ability to understand potential emerging risks.
Arceo AI helps insurers analyze their portfolios to optimize pricing and determine cybersecurity risks within a book of business. This allows insurers to automate policy binding and pricing recommendation while simultaneously outsourcing out-of-band applications through a referral process.
Data analysis tools
Legacy insurance companies with robust historical datasets coulddevelop valuable underwriting capabilities if used properly. Groundspeed relies on Artificial Intelligence & ML and text mining to help commercial insurers extract value from internal unstructured datasets such as application submissions, written policies, exposure schedules, and loss runs. This data has the potential to help insurers improve loss ratios, customer retention, and underwriting capabilities.
Habit Analytics provides an AI data analytics platform that gathers and analyzes data from IoT devices, phones, and other data sources to deliver customer insights for insurance underwriting.
Insurance securitization
Insurance securitization allows insurers to transfer underwritingrisks to the capital markets by creating tradeable financial instruments with cash flows tied to premium payments. Securitizing premium payments can generate upfront capital for insurers for regulatory compliance, funding operations, or reinforcing insurance capacity. However, the process is complicated and entails several areas of expertise including risk management, compliance, market monitoring, and valuation.
Startups such as Ledger Investing seek to provide an end-to-end securitization platform to make it easier for insurers to securitize insurance products.
Managing financial resources and balance sheets
We believe that this area withinunderwriting is significantly underserved. There is a gap in the market for technology products and services which help manage the capital for insurers.
………………………..










Comments are closed.