
GlobalData’s SME Insurance Survey indicates that almost 50% of medium-sized enterprises are aware that the cyber risks they face have increased since the pandemic. Affordable insurance cyber cover may be the answer.
Medium-sized companies are most aware of the growing risks – 49.3% stated their cyber risks have increased, to some extent, since the pandemic began.
The Insurance Survey shows that many SMEs are aware of the increasing cyber risks they are facing since the onset of the pandemic.
Realization is changing the dynamic of cyber risk management, pushing damage limitation to the forefront and, as a result, turning the spotlight on attack detection.
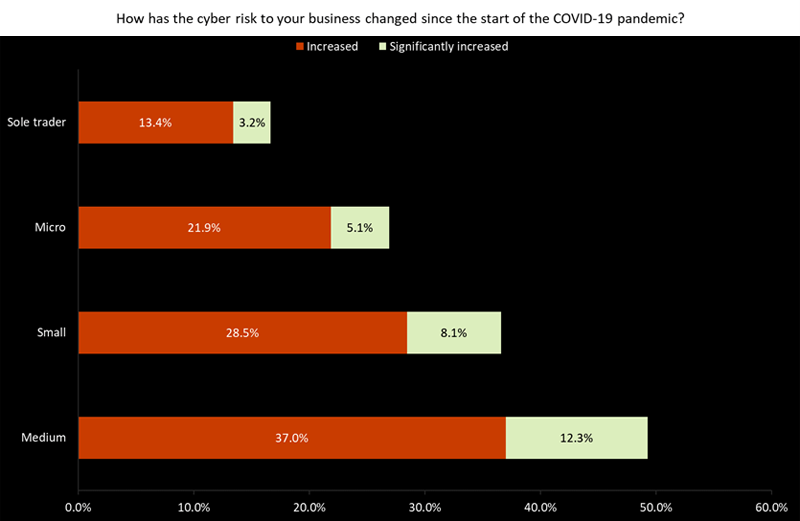
This figure decreases with business size, with 36.6% of small companies, 27% of microenterprises, and 16.6% of sole traders indicating the same.
Detecting when a malicious actor has access, or is attempting to gain access, to an organization’s systems is the foundation on which response and recovery are built.
And it is an element whose benefit can be measured in cash. The average cost of a cyber breach lasting 200 days or more was $4.86 million, technology company IBM said in its “Cost Of A Data Breach Report“.
Sums like that underline the importance of detection to companies’ cyber risk management, according to Beinsure Cyber Risk Detection Survey. And they highlight why S&P Global Ratings considers effective cyber detection to be integral to cyber risk management and ultimately a potential factor in the assessment of issuers’ credit worthiness.

Cyber insurance is no longer deemed a nice-to-have accessory for businesses. In 2023, its importance will only increase, as coverage becomes a seal of approval, indicating the organisation’s strong cyber security posture to customers, partners and peers.
According to Cyber Insurance Trends, to attain coverage, businesses need to demonstrate good ‘cyber health’ credentials in the first place – creating a vicious cycle where neither goal can be reached without achieving the other.
According to a survey run by Datto in 2023, many of the reasons companies experience cybersecurity issues are due to human error rather than flawed defense systems.
Leading reasons respondents gave for cybersecurity issues were phishing emails (37%), malicious websites (27%), weak passwords (24%), poor user practice (24%), and lack of cybersecurity training for the end user (23%) and administrator (19%).
This suggests that user training and good cybersecurity practice should remain the key focuses for businesses when dealing with cyber threats.

 by
by 


