Insurers and reinsurers leveraged alternative capital in 2023 more than any year in the history of the reinsurance market. In 2023, alternative capital crossed the $100 billion threshold, representing an increase of more than 7% from the year prior, according to AON Q4 2023 Quarterly ILS Report. As property reinsurance pricing exceeded levels not seen in several years, insurers and reinsurers were grateful for the opportunity to diversify their purchase with Insurance-Linked Securities.
ILS investors benefited from the highest risk-adjusted margins in over a decade, offering well-priced capacity to cedents during a year in which the North Atlantic hurricane season resulted in muted losses, further enhancing returns. Elevated risk-adjusted margins along with strong collateral returns have provided the best performing years in the market’s 20-plus year history. Much of the growth has been directed to the catastrophe bond market.
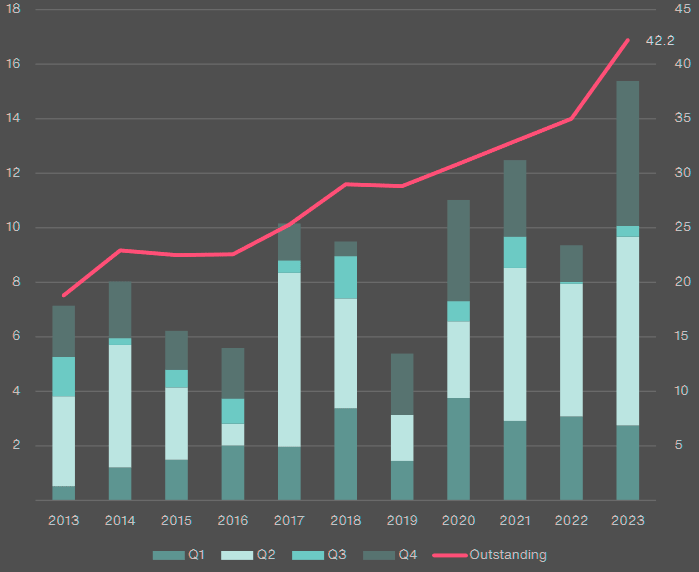
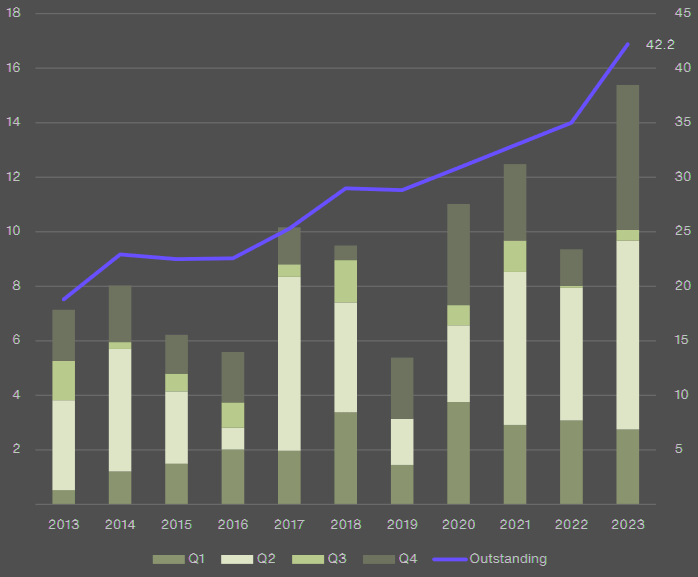
In 2023, the catastrophe bond market grew by over USD 7 billion – a 21% increase in the outstanding issuance amount.
The outstanding catastrophe bond market at year-end 2023 stood at over USD 42 billion – an all-time high. 2023 broke the record for the largest-ever level of catastrophe bond issuance, at USD 15.4 billion, and the market serviced 30 issuing insurers and 14 issuing reinsurers, with a combined amount of USD 10.1 billion.
Primary ILS Market

Government entities issued a significant amount of catastrophe bonds in 2023, totaling USD 4.8 billion. Notably, the California Earthquake Authority issued USD 1.505 billion in catastrophe bonds, the highest annual amount for any issuer since the inception of this market. The year also welcomed 11 new sponsors to the market, alongside the return of entities such as Chubb and The Hartford after several years.
The last quarter of 2023 was particularly robust, contributing USD 5.2 billion to the total issuance volume, surpassing the previous record for a fourth quarter set in 2021 by USD 2.4 billion.
Throughout 2023, the pricing for catastrophe bonds tightened, with industry loss index catastrophe bond pricing decreasing by up to 40% by June. However, pricing stabilized in the fourth quarter due to an influx of new issuances and some insurance-linked securities investors reallocating capital after a profitable year.
Despite these dynamics, companies seeking capacity in the catastrophe bond market found advantageous terms, offering a diversified and multi-year capacity compared to traditional reinsurance.
Property Catastrophe Bond Issuance and Outstanding
The fourth quarter marked a notable period for peak peril issuances, both through industry indexes and on an indemnity basis. New sponsors entered the market, including Selective Insurance and Beazley.
The Hartford returned for the first time since 2011 and successfully launched its first indemnity-triggered catastrophe bond. All mentioned transactions notably featured significant commercial exposure, which investors received positively.

The quarter witnessed an increase in diversifying transactions compared to the previous three quarters, with €805 million of European securities issued.
This included a significant issuance by Versicherungskammer Bayern Versicherungsanstalt des öffentlichen Rechts (VKB), marking the first entry of a domestic German insurance company into the market.
The robust activity in European transactions reflects the region’s insurers’ demand for additional reinsurance capacity amid a tightening reinsurance market. Current spread levels for European risks are broader than before, partly due to uncertainties related to secondary perils.
Property Catastrophe Bonds Issued and Outstanding by Quarter
The most significant catastrophe bond market development during the fourth quarter was the pioneering of cyber catastrophe bonds. AXIS placed the market’s first-ever 144A cyber catastrophe bond, an occurrence indemnity-triggered transaction, giving coverage to AXIS for losses from “systemic cyber events” over the span of a two-year risk period.
Both Beazley and Chubb followed close behind, with Chubb achieving the largest size (USD 150 million) for this new class of risk. In total, USD 415 million of cyber notional limit has been placed with catastrophe bond investors.
ILS investors are now leading the way in further developing a catastrophe market for cyber. Aon is optimistic this market will continue to develop and provide insurers with much-needed capacity to further enable the growth of the cyber insurance market.
Simultaneously, the emergence of this new class of risk creates an opportunity for catastrophe bond investors to diversify their portfolios, which are currently concentrated in natural catastrophe risk.
Last but not least, sidecar investors have been handsomely rewarded for their commitment to the product in 2023. Given strong underlying reinsurance margins and the absence of major global natural catastrophes in 2023, sidecar investors have in some cases achieved returns of more than 30%.
Renewals have therefore been relatively straightforward, as investors have been willing to commit to another year of similarly well-margined underlying reinsurance business.
Secondary ILS Market

The fourth quarter of 2023 saw a notable increase in the secondary trading of catastrophe bonds, making it the busiest in the last four years. The trading dynamics evolved significantly during this period.
In October, trading opened with a high supply as investors repositioned in anticipation of a robust new issuance pipeline.
By December, demand surged as investors who had not fully allocated their capital in the primary market turned to the secondary market to invest their remaining funds. November emerged as the most balanced month, with active selling to free up cash for new issuances and strong buying supported by surplus cash inflows.
The demand for index bonds remained robust, continuing a trend from earlier in the year.
Notably, bonds exposed to risks in the Northeast US, California earthquakes, and Europe were actively traded, albeit at slightly wider spreads than in the previous quarter due to the increased volume of primary issues involving these risks.
Overall, trading volumes in the fourth quarter of 2023 were roughly double those of the same period in 2022, when the market was still adjusting to the impacts of Hurricane Ian.
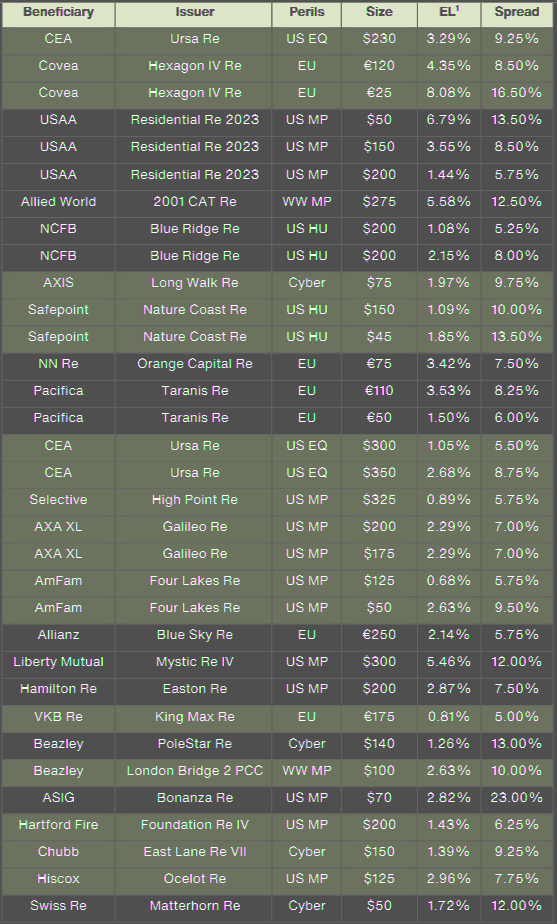
Q4 2023 144A Issuances
Macrotrends such as automation, artificial intelligence, climate change, and the green transition are reshaping our world and introducing new risks in property-casualty insurance. These changes carry significant consequences for the insurance industry.
Parametric insurance, unlike traditional models that compensate based on the actual loss, bases its structure and pricing on the likelihood of a specified event occurring.
It provides a payout when predefined criteria, such as certain wind speeds or temperatures, are met. This method also applies to other scenarios like market indices, crop yields, or power outages. A key feature of parametric insurance is its transparent and swift payment process.
Parametric solutions are becoming increasingly relevant in the renewable energy sector, especially for large-scale solar parks often located in hazard-prone areas. Traditional insurance often fails to meet the financial limits required by lenders and project financiers, but parametric insurance can offer substantial capital that traditional models cannot, thereby preventing project cancellations.

Parametric insurance has potential applications in CO2 capture projects, covering aspects from capture and transportation to storage and use.
In marine cargo parametric insurance could compensate for delays in transporting CO2 or failure to deliver, addressing significant risks including natural disasters and other challenges.
Sustainability, nature and biodiversity loss is a growing socio-economic issue whereby costly restoration is required – even mandated. Parametric policies have already been pioneered whereby a trigger, such as wind speed in a defined location, facilitates a fast payout for immediate damage assessments, debris removal and repairs to be made. Other examples could be wildfire protection for forests or protection of wetlands against drought.
The manifold emerging risks facing businesses and society shouldn’t be seen purely from a potential loss point of view. Transformative change brings uncertainty and volatility, and therefore new demand for protection.
To fulfil its role as financial shock absorbers – and to stay relevant – the re/insurance industry must respond with innovative risk solutions. Importantly, such products must also be attractive to a range of capital providers. We think parametric insurance fits the bill, helping insurers to navigate the new areas of volatility arising from evolving megatrends, and maintain business resilience.
…………………….
AUTHOR: Richard Pennay – CEO Insurance-Linked Securities Aon Securities








