
Indonesian insurance market is forecast to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9% from $5.3 billion in 2023 to $7.1 billion in 2027, in terms of gross written premiums (GWP).
According to GlobalData’s Insurance Database, Indonesia’s general insurance industry is estimated to grow by 10.2% in 2022 and 8% in 2023, supported by a rise in demand for property insurance policies due to recurring natural catastrophic (NatCat) events as well as strong economic growth.
The gross premium created (GPW) for credit insurance, the market’s third-largest business line, increased by 86.2% to IDR 5.7 billion in 2020. Property insurance, the biggest business segment, also posted solid GPW growth of 9.7% to IDR 20.9 trillion. However, motor insurance GPW recorded quiet growth of 0.3%. Improved underwriting discipline continued rate rises, lower catastrophe risks, and an improving commercial and personal auto market.
Property insurance is the largest general insurance line, which is expected to account for a 34.5% share in terms of GWP in 2023.
It is expected to grow at a CAGR of 8.6% over 2023-2027. Growth in residential property sales and the country’s increased exposure to recurring NatCat events will drive the growth of property insurance in the country.
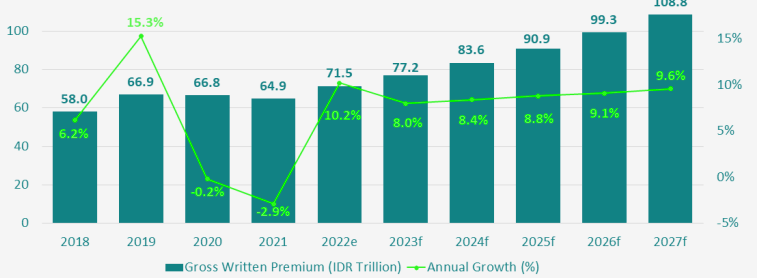
The Indonesian general insurance industry rebounded strongly in 2022 after declining for two consecutive years. The growth is driven by a strong economic recovery and increased frequency of extreme weather events that have led to an increase in the demand for natural catastrophic insurance products.
Indonesia recorded 3,544 NatCat events in 2022, including 28 earthquakes, 1,531 floods, and 1,068 other extreme weather events.
This caused damages to 95,403 properties, including severe damages to 20,205 properties, resulting in an estimated incurred loss of IDR2.2 trillion ($151.1 million) for property insurance companies in 2022.
Financial lines insurance is the second-largest insurance line, which is expected to account for a 22.1% share of general insurance premiums in 2023. It is projected to grow by 10.4% in 2023, supported by a growing economy that is driving the growth of credit insurance.
The country’s central bank, retail and commercial credit is forecast to grow by 8.9% in 2023, which will have a positive impact on credit insurance premiums.
Motor insurance is the third-largest line, which is expected to account for a 17.7% share of general insurance GWP in 2023. It is expected to register a slower growth of 6.7% in 2023 as compared to 7.1% growth in 2022 due to an expected slowdown in vehicle sales.
Other insurance lines including liability, personal accident and health (PA&H), marine, aviation, and transit (MAT) will account for the remaining 25.7% share of GWP in 2023.
High NatCat-related losses are a cause of concern for Indonesian insurers. However, companies are also expected to increase premium rates, which will support growth in the industry over the next five years. The industry’s growth will also be further supported by a strong economic upswing.
Furthermore, these factors have led to strong underwriting success in the Indonesian property and casualty insurance industry.
Indonesia’s insurance sector produces less than 1% of the country’s gross domestic product (GDP). Its penetration and density rates are below the standard for the region.
With gross insurance premiums at 1.99% of GDP versus 3.9% on average for Emerging Asia and insurance density to the tune of USD 82 per capita versus USD 207 for Emerging Asia, the industry has a lot of room for development. Some 152 insurance companies and 227 insurance intermediaries operating in the country, according to data from March 2023.
Life insurance is the biggest segment, earning 40% of total gross insurance premiums in 2023. Next comes social insurance with a 39% share and non-life insurance and reinsurance with 19% of the total. Mandatory insurance accounted for 2.6% of overall premiums. Gross contributions from Sharia insurance were equivalent to 3.2% of total insurance income.
Fact checked 




