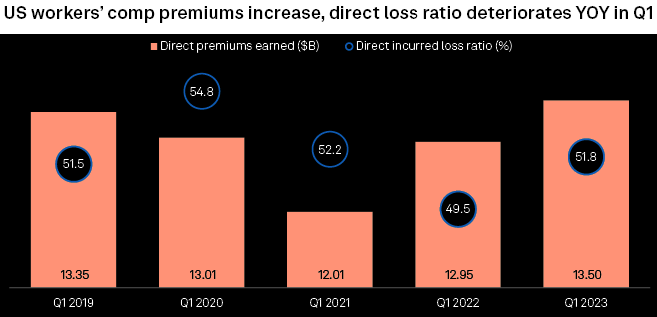
US workers’ compensation direct premiums earned rose 4.3% year over year in the first quarter, and the industry’s overall direct loss ratio deteriorated by 2.3 percentage points. Direct premiums earned grew to $13.5 billion from $12.95 billion a year earlier, according to an S&P Global Market Intelligence analysis.
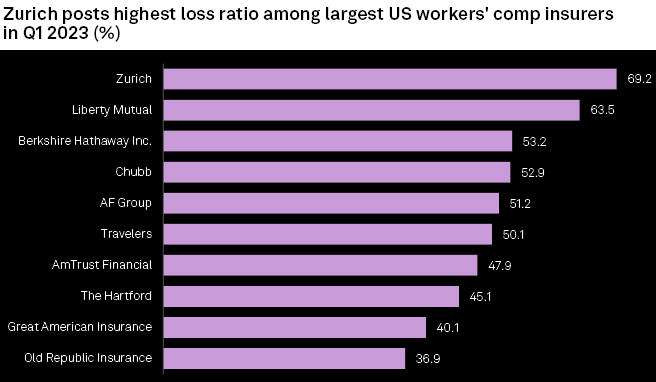
Zurich Insurance Group and Liberty Mutual Holding reported the highest direct incurred loss ratios for workers’ compensation in the first quarter of 2023, a period in which the business line’s loss ratios deteriorated year over year.

Zurich logged the worst loss ratio for the first quarter at 69.2%, a sharp increase from 54.1% a year earlier (see US Commercial Insurance Revenue).
Liberty Mutual followed closely behind with a first-quarter loss ratio of 63.5%, a much more modest increase from the 62.3% posted in the first quarter of 2022.
What is workers’ compensation?
Workers’ compensation insurance provides medical and wage benefits to people who are injured or become ill at work. The coverage is mandated by each state and the wage and medical benefits vary by state.
Workers’ compensation is considered a social insurance because it relies on a social contract between management and labor, wherein exchange for purchasing workers’ compensation insurance, business owners are protected from civil suits from their workers who become injured on the job.
Yet each party benefits has limitations. Workers’ compensation insurance is purchased by businesses, and is underwritten by insurance companies and, in some states, underwritten by publicly supported state funds.
U.S. workers’ compensation insurance premiums
While most insurers saw workers’ comp loss ratios deteriorate year over year, a handful managed to eke out some better results.
The Travelers, The Hartford Financial Services Group, AF Group and Old Republic International all saw year-over-year improvement in their first-quarter loss ratios, with favorable prior-year reserve development helping some of those names.
The Hartford’s loss ratio improved 2.2 percentage points year over year to 45.1% in the first quarter. In a recent regulatory filing, The Hartford said it decreased reserves for the 2014 to 2019 accident years, mostly in the small commercial space. The change was driven by claim severity that was lower than previously estimated.
Travelers booked the largest improvement in its first-quarter loss ratio, which declined 7.2 percentage points year over year to 50.1%.
U.S. workers’ compensation loss ratio
Net favorable prior-year reserve development amounted to $19 million in the first quarter, which was driven by a better-than-expected loss experience in the domestic operations workers’ compensation line for multiple accident years, according to a regulatory filing.
On the flip side, Chubb Ltd. saw the most significant year-over-year deterioration in its workers’ compensation loss ratio among all companies in this analysis. Chubb’s first-quarter loss ratio came in at 52.9%, much worse than the 34.7% recorded a year earlier.
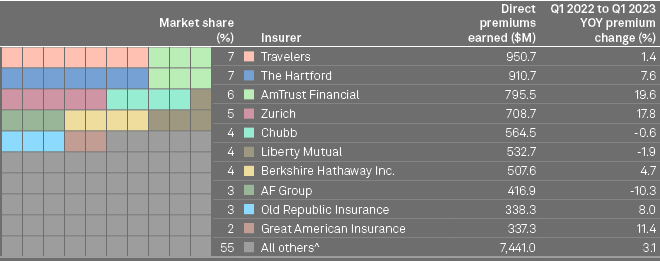
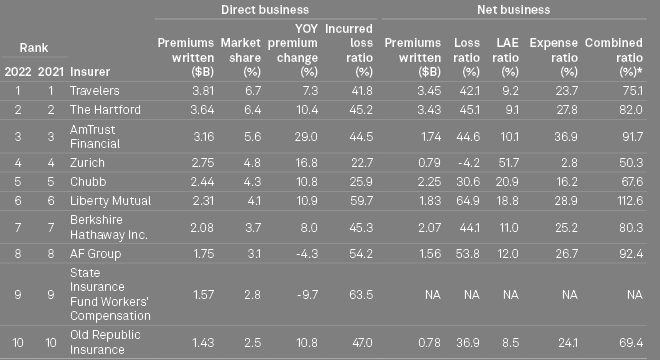
Largest insurers of workers’ compensation in the US
Travelers kept its position as the largest writer of workers’ compensation in the US in the first quarter of 2023, with $950.7 million in direct premiums earned. It was followed closely by The Hartford, which claimed second place, with $910.7 million in direct premiums earned.
The Hartford and Travelers both control about 7% of the overall workers’ compensation market each, while AmTrust Financial’s 6% of the market makes it the third-largest insurer in the business line.
Largest US workers’ insurers
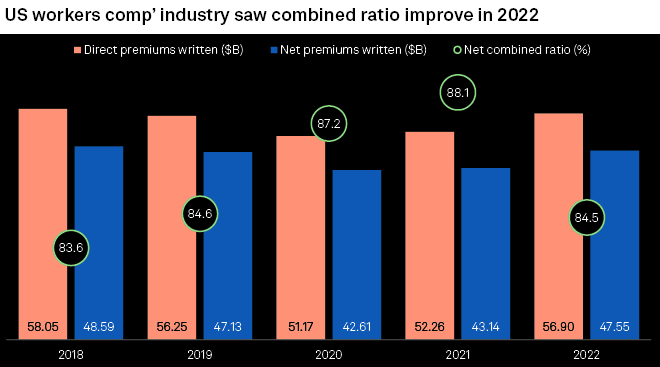
Combined ratios improved
US insurers’ combined ratios in the workers’ compensation business line improved for full year 2022 compared to the prior year.
The industry had a combined ratio of 84.5% for 2022, an improvement from 88.1% in 2021.
TOP-10 Largest US workers’ insurers by premiums
How is the cost of workers’ compensation insurance determined?
Similar businesses in each state, that exhibit comparable workplace injury patterns and costs, are grouped into classes.
Rates are determined for each class based on the prior five years of loss costs for all businesses within that class.
This provides an equitable system where rates are charged commensurate with the actual loss experience of the class of business. Economic factors for each state are then overlaid onto this data to determine the rate for each class in a given state.
A system called “experience rating” allows for modification of the class rates based on the loss history of an individual business. This system provides business owners a significant amount of control over the cost of their workers’ compensation premium – safe businesses are rewarded with lower premiums and unsafe businesses are penalized with higher premiums.
Who is required to carry workers’ compensation insurance?
All states, with a small number of exceptions, require businesses with employees who are not owners, to purchased workers’ compensation coverage for those employees.
Businesses that fail to provide workers’ compensation coverage can face severe and costly repercussions including payment of claims out of pocket, fines and possible imprisonment, as well as possibly losing the right to conduct business in the state.

How workers’ compensation claims work?
The injured parties must visit a healthcare professional immediately so a doctor can provide medical reports to support any claims.
Employees can then begin the claims filing process with insurer, being sure to include any state-mandated paperwork or forms. Once these claims are approved, the recipient will receive their compensation payments and can return to work when they feel they are ready.
……………………..
AUTHORS: Hailey Ross, Kris Elaine Figuracion – S&P Global Market Intelligence analytics








