Cyber insurance is a complex product that demands specialized knowledge and expertise. Despite these challenges, it also presents opportunities for profitable expansion and innovation within the insurance sector, according to AM Best.
The cyber insurance market has seen increasing premium rates following a surge in claims related to the pandemic.
Although recent trends suggest a stabilization or decrease in rate hikes, the market still offers appealing pricing for insurers.
AM Best released a report indicating that the expansion of cyber insurance offerings could pose significant risks to the financial stability of re/insurers if not managed with caution and continuous oversight.
According to Cyber Insurance Market Dynamics Report, economic vitality, business continuity, and successful digitalization rely on cyber coverage – and a sustainable cyber insurance market demands transparency.
Future cyberattacks will be increasingly accelerated by key technology trends such as artificial intelligence like ChatGPT, the so-called “metaverse” and the expanding worlds of IT, Internet of Things and operational technology.
All these converging technologies offer great opportunities for society, businesses and governments, though new attack surfaces, vulnerabilities and systemic risks will continue to emerge at the same time.
Cyber Re/Insurance Underwriting

The industry’s approach to underwriting cyber insurance varies. Some insurers remain wary of increasing their cyber risk exposure, with a few looking to decrease their presence in this area. In contrast, others view cyber insurance as a promising area for growth.
This diversity in approach is also evident among reinsurers, with different levels of enthusiasm for incorporating cyber risk into their portfolios. Some are actively seeking to add cyber insurance to their product mix, while others are more reserved.
When it comes to underwriting strategies for cyber risk, reinsurers often prefer arrangements based on a quota share model with a cap on the loss ratio, rather than relying on excess of loss coverage.
There is a focus on crafting policies that mirror primary insurance terms closely, including the application of exclusions to manage risk exposure in line with their risk appetite.
Advanced cyber practices remain out of reach for many issuers, and survey responses raise questions about the effectiveness of some cyber initiatives. Analysts expect cybersecurity spending to continue its run of sustained growth, a trend fueled by the persistent threat of cyberattacks, the demands of hybrid work and increased data privacy and governance regulations, according to Moody’s Cyber survey.
The agency includes evaluations of an insurer’s ability to assess and manage cyber loss potential within its rating process. It considers the impact of cyber risks on an insurer’s capital management and allocation strategies.
AM Best has observed a growing awareness within the industry of the potential for significant cyber-related losses. However, it notes that, compared to other catastrophic risks, the potential for cyber-related catastrophic losses is generally perceived to be lower at this stage.
IDC forecasts low double-digit spending increases across all industries and company size segments in the next three years. Industries expected to increase spending at the fastest rate through 2026 include securities and investment services, telecommunications, banking and insurance (see Challenges for Cyber Insurance Market).
Expansion of Cyber Insurance Offerings

The expansion of cyber insurance offerings is a response to the increasing demand for protection against cyber threats, a trend accelerated by the digital transformation of businesses and the rising sophistication of cyber attackers.
However, this expansion is not without its challenges and could pose significant risks to insurers if not managed with prudence and foresight (see How Insurers Can Expand the Cyber Insurance Market?).
The report examines how insurers and reinsurers are incorporating considerations of cyber risk into their reinsurance and retrocessional strategies, including the adoption of risk transfer mechanisms to safeguard their financial positions.
While cyber insurance offers opportunities for growth and innovation, it requires careful management due to its complex nature. Insurers and reinsurers are taking varied approaches to this line of business, reflecting differing levels of risk tolerance.
AM Best emphasizes the importance of integrating cyber risk considerations into broader capital management and risk mitigation strategies to maintain financial resilience.
Cyber Insurance Market Growth and Implications

The cyber insurance market has grown significantly, driven by the recognition of cyber threats as a critical business risk, according to Beinsure cyber insurance syrvey.
This growth reflects an increasing awareness among businesses of the potential financial and reputational damages caused by cyber incidents, such as data breaches, ransomware attacks, and system outages.
As companies seek coverage to mitigate these risks, insurers have responded by expanding their cyber insurance offerings.
- Economic costs of cyber-crime will reach $24 trillion by 2027
- 83% of C-level executives of global survey respondents felt inadequately protected against cybercrime
- 38% of C-level executives of survey respondents were extremely concerned about potential cyberattacks
By applying discipline and acuity to risk management, we can contribute to a sustainable cyber insurance market, protect businesses, and humanity’s interconnectedness into the future.
In addition to the growing sophistication of cyber-criminal activities, organisations worldwide face greater exposure than ever to geopolitical conflicts, which are already starting to have an unprecedented impact on cybersecurity.
Global cyber insurance market outlook
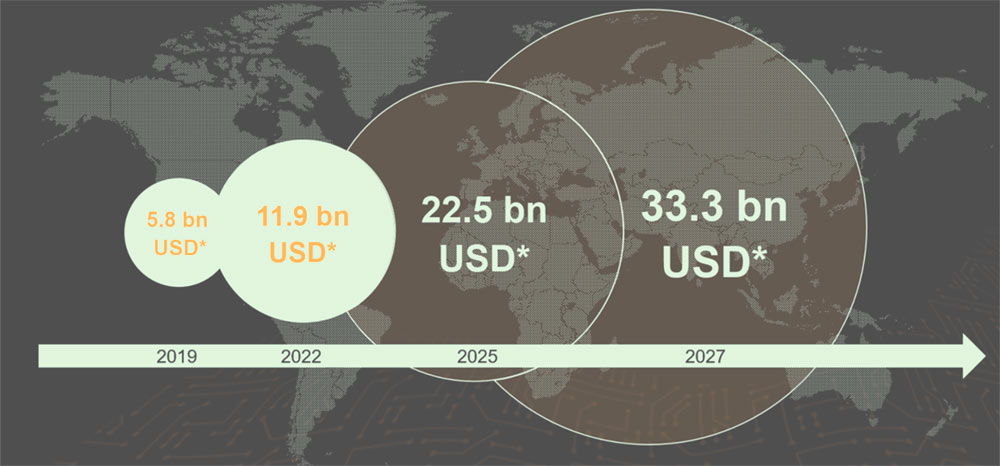
Cyber risk management is core in a digitised world. Since cyber insurance is an essential part of this, demand continues to grow strongly.
Facilitating a sustainable cyber insurance market remains a key task for the insurance industry.
Risk Assessment Challenges
One of the primary risks associated with the expansion of cyber insurance is the difficulty in accurately assessing and pricing cyber risks.
Unlike traditional insurance categories, where historical data can inform risk assessments, the cyber landscape is rapidly evolving.
The nature and scale of threats change quickly, making it challenging to use past events as reliable predictors of future risks. This uncertainty can lead to mispriced policies, potentially exposing insurers to higher-than-anticipated claims.
- Cybersecurity spending rose by 70%, over the past four years (response rate: 27%). There was considerable variance in growth rates among respondents, but budgets were up overall, and significantly for most sectors. Budgets for corporates grew the most — up 100%.
- Overall, issuers say they devoted a median of 8% of their technology budgets to cybersecurity in the survey (response rate of 36% to 47%), up from 5%. The increase is likely a response to rapid digitalization and an accompanying rise in cyber risk in recent years. A shift to remote work during the COVID-19 pandemic has also broadened issuers’ digital footprints and opened new channels for cyberattacks.
Cybersecurity is typically more resilient to economic pressure than other technology-related budget items because companies must often meet certain compliance and regulatory requirements or minimum spending levels to qualify for cyber insurance.
Accumulation & Silent Cyber Risk

Cyber risks are uniquely challenging due to their potential for accumulation. A single cyber event can affect multiple policyholders simultaneously, especially if they share common vulnerabilities or rely on the same technology providers.
This interconnectedness can lead to significant aggregated losses for insurers, exceeding their expectations and capacity. The systemic nature of cyber risk, exemplified by widespread software vulnerabilities or major service provider outages, amplifies this accumulation risk.
Another concern is the issue of silent cyber risk, where cyber exposures may be inadvertently covered in policies not explicitly designed for cyber risks.
As businesses and operations become increasingly digitized, traditional policies such as property or liability insurance might be called upon to cover cyber-related losses. This unintended coverage can expose insurers to unexpected claims, complicating risk management and financial planning.
Legal and Regulatory Environment
The legal and regulatory landscape surrounding cyber risk is also evolving. As governments worldwide introduce stricter data protection regulations, the potential liabilities for businesses experiencing data breaches have increased.
This evolving regulatory environment adds another layer of complexity to underwriting cyber insurance, as insurers must continually adapt their policies to comply with new laws and understand their implications for coverage.
Strategies for Mitigating Cyber Risks

To navigate these challenges, insurers are adopting various strategies. These include enhancing their cyber risk assessment capabilities through advanced analytics, artificial intelligence, and collaboration with cybersecurity firms.
Insurers are also refining their underwriting processes, introducing more rigorous criteria, and developing specialized cyber insurance products that more accurately reflect the risk landscape.
Moreover, insurers are actively managing accumulation risk by setting clear limits on coverage, diversifying their portfolios, and employing reinsurance to spread the risk. To address silent cyber risk, insurers are clarifying policy wordings to specify the extent of cyber coverage in traditional policies.
The expansion of cyber insurance offerings represents a significant opportunity for insurers to meet the growing demand for cyber risk protection.
However, it introduces complex challenges that require sophisticated risk assessment and management strategies. By carefully navigating these risks, insurers can contribute to a more resilient cyber ecosystem while ensuring their own financial stability and sustainability in this rapidly evolving market.
…………………..
AUTHOR: Oleg Parashchak – CEO Finance Media Holding








