In 2024, the U.S. cyber insurance market experienced its second consecutive year of strong underwriting profits, according to Fitch Ratings. However, the volume of written insurance premiums remained stagnant due to renewed pricing pressure.
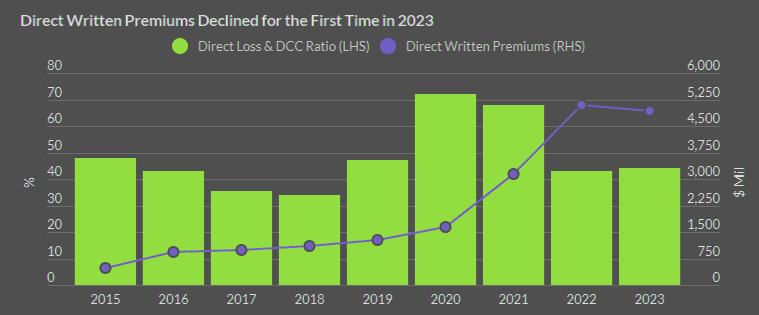
Analysis of preliminary data from cyber insurance supplemental filings reveals that in 2023, the direct incurred loss and defense and cost containment expenses ratio for standalone cyber coverage remained stable at 44%, compared to 43% in 2023.
The stability comes after less favorable outcomes in 2020 and 2021, with the ratio maintaining a profitable average of 48% over the past nine years.
The positive underwriting results stem from significant previous increases in premium rates and a more selective approach to cyber risk by insurers.
Cyber insurance penetration and associated resilience need to be further increased. This report provides an outlook on the cyber risk landscape and the surrounding dynamics affecting cyber insurance.
In a digitalised global economy, insurers contribute significantly when protecting businesses against the cyber risks they face.
Cyber hygiene and risk management

Insurers now require potential clients to implement robust cyber hygiene and risk management practices as a precondition for coverage. They have also made policy terms more stringent, frequently including sub-limits and exclusions to manage exposure more effectively.
Despite ongoing demand for current cyber risk landscape, U.S. statutory direct written insurance premiums for both standalone and package policies declined by 2% in 2023—the first recorded decrease.
Allianz analysis of a number of large insurance cyber losses shows that the proportion of cases in which data is exfiltrated is increasing every year – from 40% of cases in 2019 to around 77% of cases in 2022, with 2023 on course to surpass last year’s total.
This downturn contrasts sharply with the approximately 200% market growth from the end of 2020 to 2022. This reversal occurred even as insurers continued to expand their cyber underwriting portfolios amid softer pricing trends.
Global cyber insurance market outlook
Cyber risk management is core in a digitised world. Since cyber insurance is an essential part of this, demand continues to grow strongly.
Facilitating a sustainable cyber insurance market remains a key task for the insurance industry.
The expansion of cyber insurance offerings is a response to the increasing demand for protection against cyber threats, a trend accelerated by the digital transformation of businesses and the rising sophistication of cyber attackers.
Standalone cyber coverage direct loss
Stand-alone cyber coverage, which represents 69% of all industry written premiums, declined by 3% in 2023 to $4.9 bn.
Current segment underwriting profitability at current levels is unsustainable as cyber insurance pricing is likely to remain flat or down going forward
According to Allianz Cyber Security Global Trends, hackers are increasingly targeting IT and physical supply chains, launching mass cyber-attacks and finding new ways to extort money from companies, large and small.
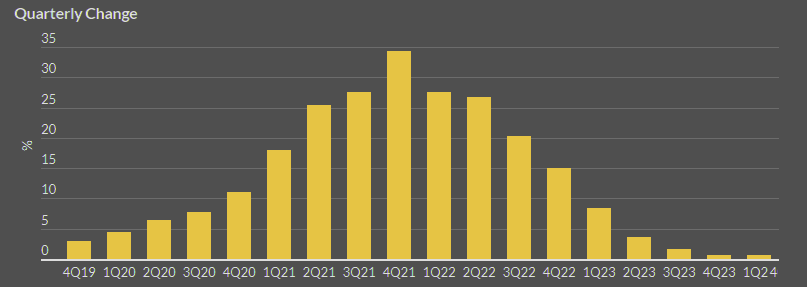
The Council of Insurance Agents & Brokers’ Commercial P&C Market Survey reveals that pricing has substantially moderated following rapid rate increases throughout 2021 and 2023. Average cyber renewal premium rate increases were up less than 1% per the 2024 survey compared with 15% and 34% in 2022 and 2021, respectively.
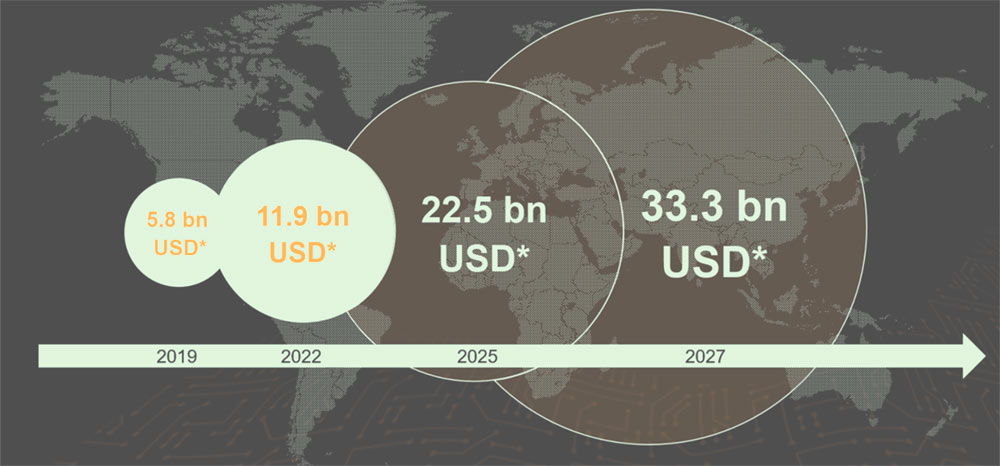
The global cyber insurance market has reached a size of $14bn in 2023 and is estimated by Munich Re to increase to around $29bn by 2027
Marsh reported that U.S. cyber renewal rates were down for the last three successive quarters, including a 4% decline, as new capacity continues to enter the market despite concerns regarding ransomware and cyber catastrophe exposure, particularly via the managing general agent channel.
Changes in cyber insurance renewal premium rates
Statutory cyber financial data does not fully reflect segment profitability because it excludes certain underwriting and adjusting expenses.
This data does not account for the effects on premiums and losses from ceded reinsurance, a common practice for cyber insurance, which primary carriers often procure significantly.
Insurance carriers are likely to encounter challenges in maintaining underwriting discipline as competition in the market grows and as they adjust to a claims environment that is rapidly changing due to technological advancements (see Cyber Insurance Poses Significant Risks).
The risk of cyber losses is further increased by the expanding regulatory and compliance demands.

Recent initiatives, such as the SEC’s cyber risk management disclosures for public companies, amplify litigation risks and the potential for significant fines if companies fail to disclose data breaches appropriately.
The uncertainty of catastrophe exposure from cyber risks presents a significant challenge, particularly in assessing the nature, likelihood, and cost of severe cyber events.
Although carriers and risk modeling firms invest heavily in tools to measure risk aggregations and probable maximum losses from major cyber events, these models are less developed than those for natural catastrophes, which have been refined over the past three decades.
According to Cyber Insurance Market Dynamics Report, economic vitality, business continuity, and successful digitalization rely on cyber coverage – and a sustainable cyber insurance market demands transparency.
Future cyberattacks will be increasingly accelerated by key technology trends such as artificial intelligence like ChatGPT, the so-called “metaverse” and the expanding worlds of IT, Internet of Things and operational technology.
All these converging technologies offer great opportunities for society, businesses and governments, though new attack surfaces, vulnerabilities and systemic risks will continue to emerge at the same time.
………………
AUTHORS: James Auden, CFA – Managing Director, North American Insurance at Fitch Ratings, Gerry Glombicki, CPA, CISSP, CCSP, CISA, ARM – Senior Director, North American Insurance at Fitch Ratings, Sarah Repucci – Senior Director at Fitch Wire








