The Korean financial performance of insurers should marginally improve in the near term, driven by a gradual rise in investment yields and a greater portion of higher value-added businesses.
Profitability should increase moderately at non-life insurers as well, thanks to improved underwriting performance and an increase in premium rates. Nonetheless, this could be somewhat offset by inflationary pressure on claims and challenged capitalisation amid interest-rate hikes.
A neutral outlook on Korea’s life and non-life insurers for 2023

According to Fitch Ratings, Korean insurers generally manage their liquidity and funding flexibility well, but sudden market volatility, along with interest rate hikes and higher inflation, could increase the insurers’ funding costs and surrender risk, particularly for endowment policies.
Insurers are likely to face more difficulties in refinancing debt and may choose to offer incentives to policyholders to hold on to policies to minimise surrender risk.
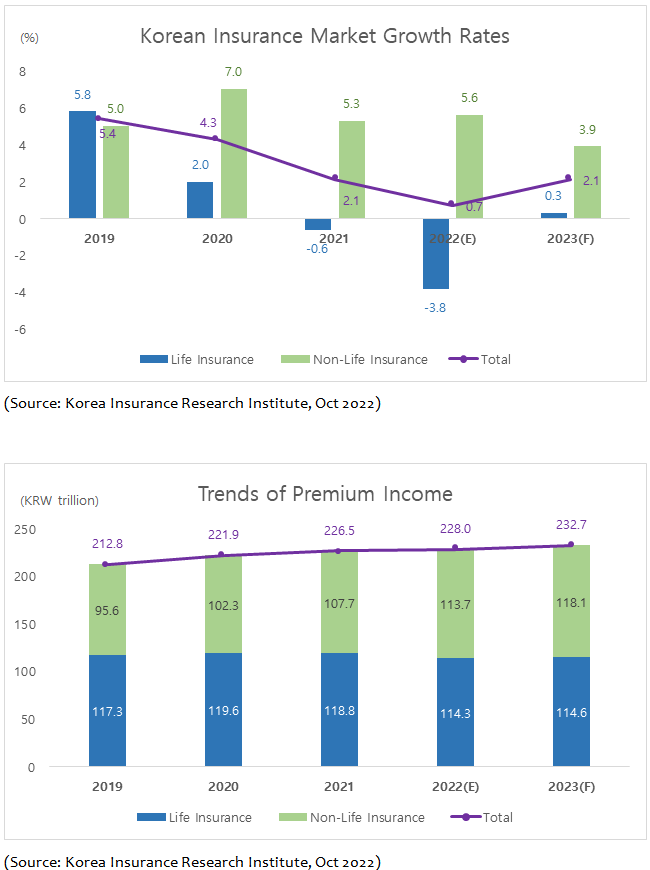
Insurance market growth in Korea is expected to recover to 2.1% in 2023 from 0.7% in 2022 with total premiums projected at over KRW 232 trln
Korea Insurance Research Institute
The non-life insurance market will continue to grow, but its growth will be moderating amid weakening economic growth prospects. Since Russia’s invasion of Ukraine in February 2022, the economy has been losing recovery momentum. Besides, consumer spending is likely to be affected by rising inflationary pressure.
As economic strength will have a direct impact on insurance market growth, insurance companies will need to keep a weather eye on economic conditions such as inflation, GDP growth, household indebtedness, and global supply chain issues.
The life insurance market is forecast to return to positive growth
The life insurance market is forecast to return to positive growth in 2023 after a sharp contraction in 2022, but the life market will likely be surpassed by the non-life market in terms of premium volume.
The life insurance market is expected to rebound in 2023 after declining for two years in a row, with premium income forecast to grow by 0.3% to KRW 114.6 trln in 2023.
Korea Insurance Research Institute
When retirement annuity premiums are excluded, however, the expected growth rate is down to minus 0.3%. Savings life insurance premiums are projected to fall by 3.4% as life insurers will continue to focus on selling protection products, but the pace of contraction will be tempered compared to the previous year.
Although rising interest rates on bank deposit products have made savings insurance look relatively less attractive, some life insurers will likely pivot toward high-guaranteed rate savings products to take advantage of interest rate hikes so that they can boost their revenues and assets.
South Korea’s general insurance market will experience healthy growth

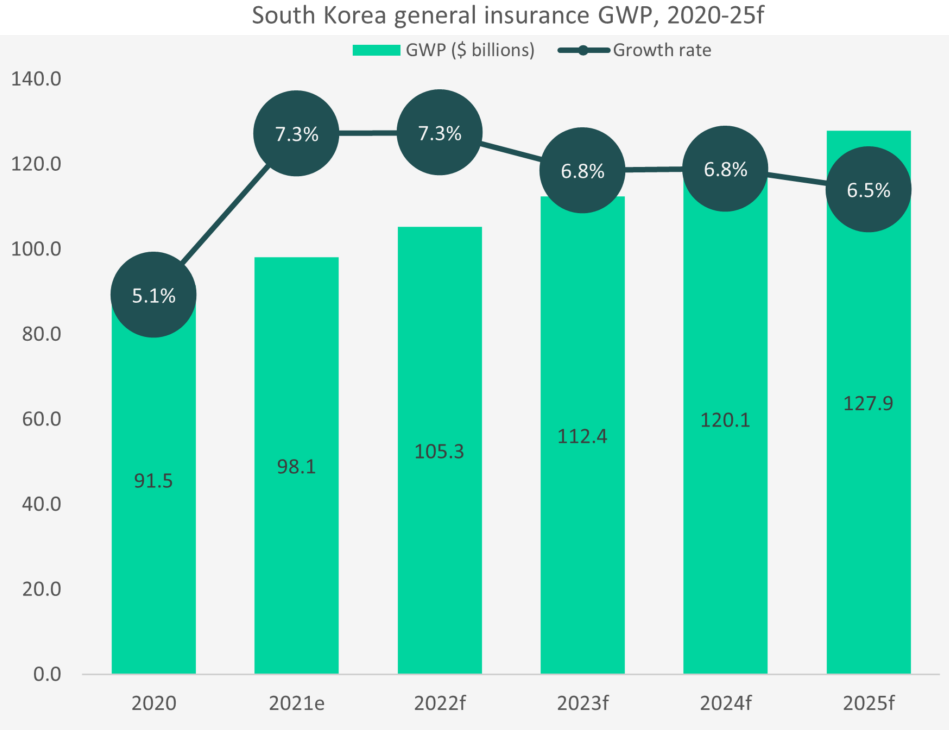
GlobalData forecasts that South Korea’s general insurance market will experience healthy growth, recording a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% over 2020–25f, making it an attractive market for foreign investment.
According to GlobalData’s Global Insurance Database, in terms of gross written premiums (GWP), South Korea’s general insurance market is set to grow from KRW112.3trn ($98.1bn) in 2021 to KRW143.9trn ($127.9bn) in 2025f, representing a CAGR of 6.8%.
Furthermore, general insurance will account for 52.2% of GWP in 2025f, compared to 48.6% in 2021e. Motor insurance leads the way with a 17.5% share of general insurance GWP.
This opportunity has prompted Ramon International to enter the market by acquiring a majority stake in CKI Korea through its parent company, Kastor Holdings. Ramon International has now been rebranded as Ramon Korea Limited as it aims to grow its credibility in the Asian market.
South Korea is one of the strongest economies in Asia, with GDP of over $1.8trn as per the IMF. That equates to roughly a 5% share of the entire Asian market. South Korea’s strong and growing economy is clearly promising to insurers and brokers, such as Ramon, in or entering into the market.
However, one of the biggest challenges they will face is the country’s declining population, which is set to fall by 13.7% by 2060 according to Statistics Korea.
A declining population would naturally mean a smaller customer base. Nonetheless, the market provides insurers with the opportunity of a growing economy and a gateway into the wider region.
Korean Commercial Insurance Market
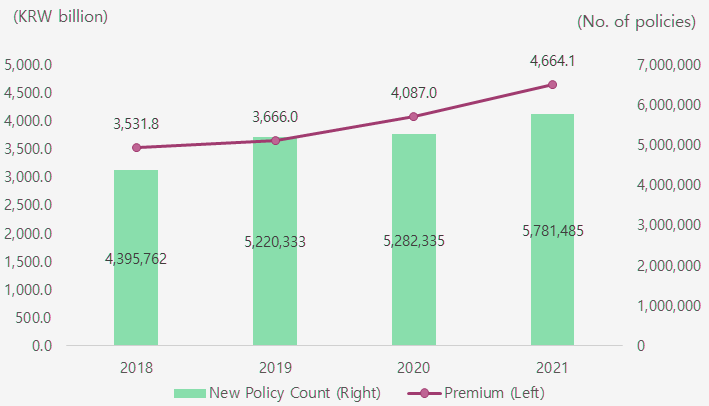
The growth of premium income for the commercial insurance market in Korea accelerated to 14.1% in 2021, with the market being valued at KRW 4,664.1 billion. All lines of commercial insurance showed strong growth except for fire insurance.
In particular, liability, engineering, and comprehensive insurance recorded double-digit growth rates. Engineering insurance recorded the highest year-on-year growth rate of 22.3%, with premiums amounting to KRW 365.4 billion in 2021.
The number of new commercial insurance policies increased by 9.4% to almost 5.8 million, with marine insurance posting the highest growth rate of 24.5%.
Commercial insurance refers to general property & casualty (P&C) insurance other than household general P&C insurance and motor insurance. It is designed to provide coverage for businesses against risks that may arise in relation to their business operations and threaten their financial stability.
Unlike personal lines of insurance, commercial insurance is corporate insurance that is structured and negotiated to meet the needs of specific corporations or industries. It provides much higher limits of coverage than personal insurance because the sum insured is typically much higher.
Commercial insurance accounted for 43.3% of the total general P&C insurance premiums, and the share has continuously increased from 41.2% in 2019 to 43.3% in 2022. On the other hand, personal insurance made up the rest 56.7% in 2022, down from 58.8% in 2020. When it comes to new policy counts, commercial insurance took up only 18.5%, but the share has also been on the rise.
The share of fire insurance continued to drop to 4.5%, with the fire coverage being increasingly packaged into comprehensive insurance. Marine insurance also saw its share fall to 15.9% as its premium growth slowed down compared to the previous year.
The share of liability insurance declined marginally but remained high at 28.9% amid the growing importance of liability coverage among companies and the government’s initiatives to introduce new compulsory insurance plans to reinforce protection of accident victims against the costs of recovering from an accident that someone else has caused. In particular, there has been an uptick in demand recently due to increasing incidences of man-made disasters and growing interest in insurance covering the commercial sector against various business risks, such as negligence claims and data breaches.
Life annuity premiums will continue to shrink
Variable life savings insurance is also faced with some headwinds. As the stock market is slumping amid concerns over economic downturns, sales of variable insurance have tumbled, and the surrender rate has increased, with premium income expected to decline by 6.9% in 2023. Despite a growing interest in investment products, the demand for variable savings insurance is likely to decline due to higher financial market volatility.
Korean Life Insurance Market Outlook 2023
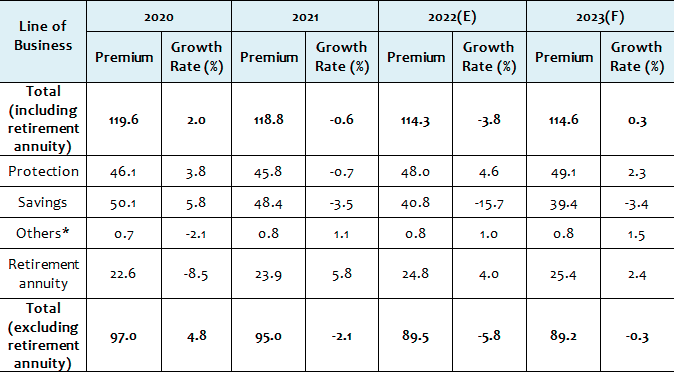
On the other hand, premiums from protection-type insurance are forecast to grow by 2.3% because sales of health insurance remain robust. The COVID-19 pandemic has become a driving force behind rising risk awareness and demand for health insurance coverage.
This will provide a greater boost to insurers’ marketing initiatives to sell protection-type products in the run-up to the implementation of IFRS 17 and K-ICS. However, economic weakness will have a negative impact on insurance sales growth as fewer consumers will have extra money to spend on insurance.
Life annuity premiums will continue to shrink as life insurers are struggling with the challenges of longevity risk management and stronger capital requirements under new accounting standards.
Still, increasing life expectancy is the primary driver that increases the demand for annuity plans, and rising crediting rates may lead to a renewed interest in annuities with an increasing number of baby boomers hitting retirement age.
The retirement annuity market in Korea
The retirement annuity market in Korea is on track to keep growing, as the demand for annuity products is rising amid a growing population of 65 years and older. However, the pace of growth is slowing because the effect of an increase in funding requirements for defined benefit plans has come to an end.
Life insurers are anticipated to see a 2.4% growth in retirement annuity in 2023, while retirement annuity premiums of non-life insurers are expected to grow by 5% on the back of premiums from in-force policies as well as new business drives by a few insurers.
Improving labor market conditions and the expansion of the individual retirement pension (IRP) sector are upside factors that drive the growth of the overall retirement annuity market. There are some downside factors for insurers, on the other hand, such as intensifying competition against other financial sectors and capital requirements for annuity reserves. Given that a large chunk of premium contributions are made at the end of the year, there is a higher level of uncertainty as to growth projections for the retirement annuity market.
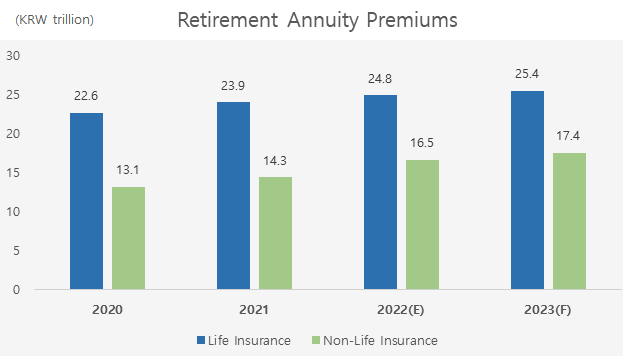
Capital strength is a key credit factor under the upcoming capital regime, K-ICS. Interest rate hikes to provide some capital buffer to insurers, as insurance liabilities will be computed by market value.
Digitalisation in the insurance industry to improve the industry’s penetration rate, but to also increase cyber security risk.
………………………..



 by
by 




