Global workplace safety has long been a critical concern for organisations worldwide, costing society over $4 trillion annually. In recent years, advancements in technology, specifically in the fields of computer vision and data science, have provided leaders with unprecedented opportunities to achieve tangible environmental, social, and governance (ESG) goals in the realm of workplace safety.
Employee safety is a top priority for businesses across all industries. Workplace injuries, physical security breaches, chemical spills, and fires not only cost businesses significant amounts of money but can also tarnish business reputations.
One AI safety technology being adopted by more companies is computer vision which enables machines to interpret visual information faster than humans can and with greater accuracy.
The use of computer vision is already common within many industries, but let’s dive deeper into how manufacturers are adopting computer vision and applying it to improve employee safety and explore real-world examples of its effectiveness.

Computer vision is becoming a powerful tool for detecting employee safety hazards earlier to prevent workplace accidents. By understanding the technology and implementing the right system, businesses can protect their employees and reap long-term benefits. By detecting hazards early and proactively addressing them, businesses create a safer and more productive work culture for their teams.
Essentially, the convergence of computer vision, data science, financial incentives, technology, and societal trends has created a unique opportunity to achieve global workplace safety.
Through the adoption of advanced technologies and data-driven approaches, organisations can prevent accidents, reduce costs, attract investment, and meet the growing expectations of their employees and consumers.
The impact of Artificial Intelligence is spreading, probably further than many people thought it might. Rapid advances in technology, the continuing talent shortage and rising customer expectations for experiences of all types have disrupted the insurance industry over the last several years, challenging carriers to evolve their service strategies and business processes accordingly.
Technological capabilities has set a digital transformation

The convergence of technological capabilities like computer vision and social trends like safety culture has set the stage for a groundbreaking transformation in occupational safety.
New AI-powered MGA players in the $715 bn commercial property & casualty insurance market can provide the financial incentives that drive necessary change, all while improving customer experiences and loss ratios
Computer vision, a field that combines artificial intelligence and image processing techniques, has made significant strides in enhancing workplace safety. At the company where I work, we have demonstrably lowered the risk of injuries (see 9 New Technology Trends by Insurance Sector: Big Data, AI & Machine learning).
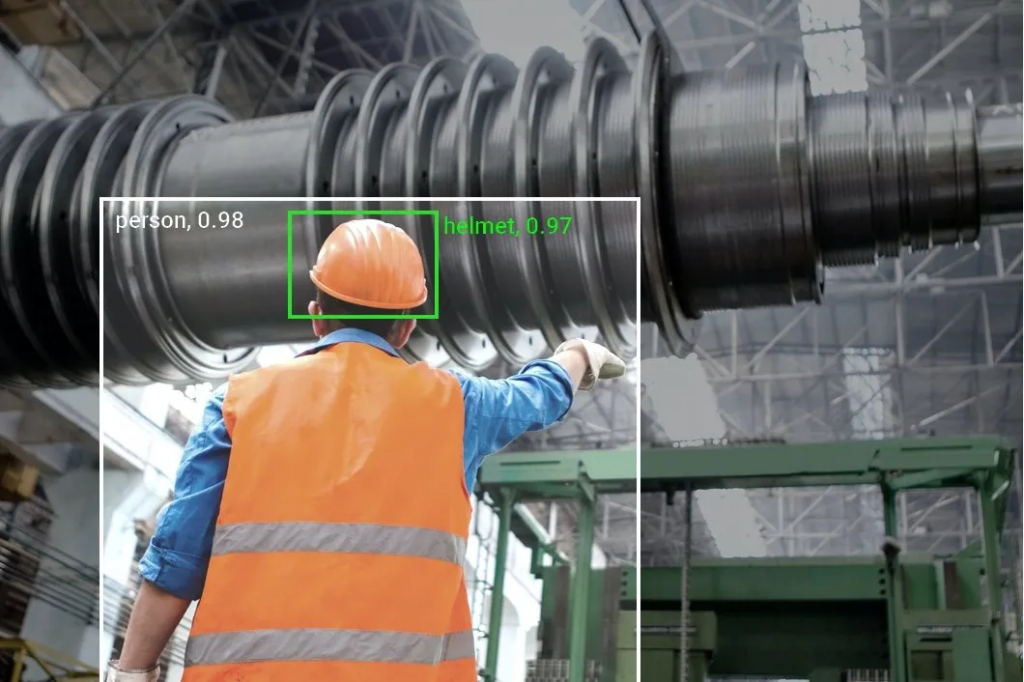
By leveraging cameras and sensors, computer vision systems can detect potential hazards and unsafe practices. For instance, they can identify workers not wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), detect near misses by forklifts, and monitor ergonomics.
This technology acts as a vigilant, non-intrusive observer, analysing and alerting workers and management to potential risks, thereby preventing accidents before they occur.
Common applications of computer vision AI for workplace safety
According to Chooch, computer vision has the potential to revolutionize workplace safety by automating hazard detection and providing real-time alerts. Computer vision helps businesses quickly identify and address safety risks, preventing accidents and improving overall employee welfare.
Employee safety hazards take many forms, depending on the industry and work environment. These are some of the more common examples where computer vision is used for early hazard detection.
How to use Computer Vision AI for Safer Workplace?
AI can provide significant advantages for manufacturers when used for quality assurance, including:
- Monitoring hazardous conditions
Extreme temperatures, gas leaks, chemical exposures, fire, and smoke can be detected at the earliest signs of leaks or spills to prevent catastrophic environmental incidents, which in the United States alone, happen once every two days costing $477M annually. - Detecting emergency response
Struck-by incidents, where workers are hit by moving objects or caught-in between accidents where individuals become trapped in machinery or equipment can be identified earlier. Enforcing zones around no-go area sand sending alerts to supervisors when people cross into such zones can provide early warning. - Identifying unsafe employee behaviors or practices
Slip and fall, firearm, and proper ergonomic detections can be detected using computer vision models installed on cameras and other edge devices. - Detecting personal protective equipment (PPE) violations
Hardhats, gloves, goggles, safety vests, harnesses are all required safety measures that ensure an organization’s compliance with regulatory agencies, computer vision models can monitor adherance automatically. - Predictive maintenance and automated inspection
Signs of wear, damage, or tampering with equipment or electrical hazards, such as exposed wiring or overloaded circuits, can be monitored automatically by static cameras or drones running defect detection AI and watching for damage in asset intensive industries.
The role of data science

Additionally, data science plays a crucial role in harnessing the power of workplace safety. By analysing vast amounts of data collected from on-site video sources, data science can identify patterns and trends that lead to injuries. Time-based heat maps for example provide insights that enable organisations to proactively address high-risk areas.
Safety professionals are empowered by these reports to implement targeted interventions, effectively mitigating potential hazards.
Moreover, predictive analytics can be employed to forecast potential safety incidents, allowing organisations to allocate resources strategically and implement preventive measures.
This data can now also be used to reduce rates for workers’ compensation insurance by measurably lowering risk. This can essentially zero-out the cost of the technology. This means that there is only upside to this transformation of safety.
The convergence of financial incentives, technology, and social trends further strengthens the drive for global workplace safety. AI-powered workers’ compensation insurance
Organizations have recognized the substantial financial benefits associated with maintaining safe workplaces. The costs of workplace injuries, including medical expenses, workers’ compensation claims, and lost productivity, can be astronomical. In the United States, the National Safety Council has calculated that in 2021 the cost of injuries was $167 Billion.
By reducing these incidents, organisations can significantly lower expenses, enhance operational efficiency, and improve their bottom line.

Additionally, investors and stakeholders increasingly prioritise ESG factors, including workplace safety, when evaluating a company’s performance and sustainability (see How Insurers are Contributing to Social Sustainability? Role of Insurance in ESG). By embracing comprehensive safety initiatives, organisations can attract investment, enhance their reputation, and foster a culture of responsibility.
Societal expectations and awareness regarding workplace safety have grown significantly in recent years.
Employees and consumers alike demand safer working conditions, and organizations are expected to align with these expectations. By prioritizing workplace safety, companies demonstrate their commitment to the well-being of their workforce, which in turn improves employee satisfaction and engagement. Workers vote with their feet, and in today’s highly competitive labor market, decreases turnover by creating a safety culture. (see How AI Technology Can Help Insurers Enhance the Customer Experience?)
Workplace accidents can have a damaging effect on brands. Consumers are becoming more conscious of the ethical practices of the organisations they support, favouring those that prioritise safety and sustainability. As a result, organisations that excel in workplace safety gain a competitive advantage and establish themselves as leaders in their industries.

Seizing this opportune moment to address preventable workplace injuries promises to benefit all stakeholders involved.
By embracing computer vision and data science technologies, organizations can not only fulfill their ESG goals but also create safer and more productive work environments.
Employees will experience reduced risks to their health and well-being, fostering a positive work culture. Moreover, organizations will witness enhanced operational efficiency, reduced costs, improved reputations, and increased stakeholder trust.
By prioritising workplace safety, we can pave the way for a future where preventable workplace injuries are minimised, benefiting all stakeholders in organisations worldwide.
……………………
AUTHOR: Josh Butler – CEO & Founder of CompScience – Vision for Injury Prevention, Fastest Growing Workers’ Comp MGA