Global Ranking of insurance providers worldwide and largest underwriters in the cyber insurance sector. Insuramore has updated its 2023 global ranking of insurer groups as measured by cyber insurance gross direct premiums written (GDPW).
Analyzed as consolidated groups, the world’s top 100 carriers (underwriters) on cyber insurance market accounted for 97.8% of total global gross direct premiums written for this category.
The cyber insurance market is anticipated to maintain favorable premium growth and underwriting results through 2023; however, pricing will likely moderate further this year in response to recent profits and competitive factors.
Industry statutory direct written premiums for cyber coverage in standalone and package policies increased by over 50% in 2022 to $7.2 bn, following 73% premium growth in the prior year.
One possible factor behind the recent smaller increases is reduced cyber claims activity. According to survey results, the number of respondents reporting an increase in cyber claims has fallen almost 20% from the previous quarter, and nearly 30% from the beginning of the year.
Cyber insurance gross direct premiums written

- Globally, over 220 insurer groups and 360 individual MGA / MGU enterprises were underwriting cyber risks by the 2023 (see Cyber Security Top Trends & Cyber Attack Threats)
- Worldwide GDPW amounted to around USD 13.5 bn with the top 20 groups in the sector accounting for over 70% of this value
- The competitive structure of the global market is becoming more fragmented due in part to the introduction of additional capacity from new sources (see about Cyber Insurance Risks & Cyberattacs in the Russia-Ukraine War)
The analysis indicates that GDPW for cyber insurance can be estimated globally at close to USD 13.5 bn rising towards USD 14 bn if captive insurers are also included, and with the US alone likely to make up over a half of the total.
With regards to the competitive structure of the market, it shows that the top 20 groups for this class are likely to have accounted for 70.3% of premiums worldwide and the top 50 for 92.3%, down from a respective 76.6% and 94.4% in 2022.
To better understand the role that detection plays in cyber risk management it helps to understand the nature of a typical cyberattack (see What are the Most Common Types of Cyberattacks?)
Top 100 Insurer Groups Worldwide by cyber insurance premiums
In the ranking, cyber insurance GDPW for each group are presented as a range of the likely minimum and likely maximum values with the midpoint of the range then used to determine the ranking and approximate global market share.
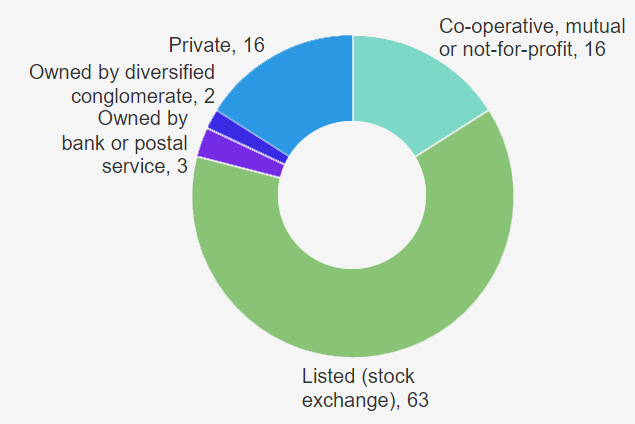
Insurers’ segmentation by type
A catastrophic cyber attack is the top scenario in 2023 resilience plans. Such an attack would surely put C-suite alliances to the test. Cybersecurity has become a more dynamic field, rapidly adjusting and shifting to keep apace with business inventiveness.
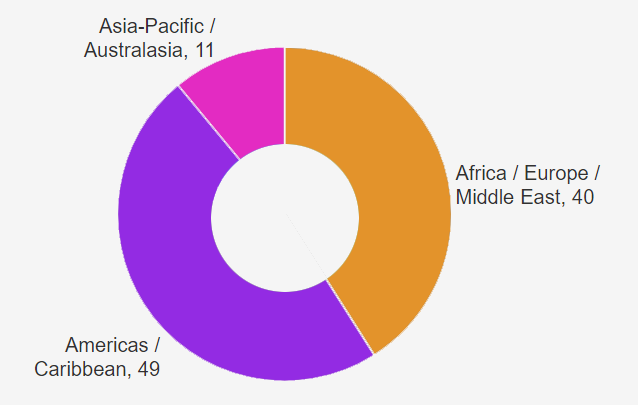
Insurers’ segmentation by regions
The research established that over 220 insurer groups were underwriting cyber risks on a direct basis by the end of 2022, up from over 180 one year previously.
Munich Re have been the global market leader with over USD 1 bn in GDPW – a figure which doubles including its cyber reinsurance premiums – and is followed in descending order by Chubb, Beazley, Fairfax Financial Holdings and AXA (see TOP 15 U.S. Cyber Insurance Companies).
TOP 5 Insurer by gross direct premiums written for cyber insurance
| Rank | Insurer | GDPW, $ mn | Global market share, % |
| 1 | Munich Re | 1 050 | 7,79% |
| 2 | Chubb | 1 000 | 7,42% |
| 3 | Beazley | 870 | 6,45% |
| 4 | Fairfax | 810 | 6,01% |
| 5 | AXA | 633 | 4,69% |
| All other insurers | 9 123 | 67,65% | |
| Global Total | 13 485 | 100,00% |
Insuramore has also identified as many as 360 individual MGA, MGU and cover-holder enterprises (a.k.a. underwriting agencies) around the world writing cyber insurance on a delegated underwriting authority basis.
Trend towards fragmentation of global cyber insurance market share continues in 2023

Looking ahead, the trend towards fragmentation implied by the preceding comparison of the global market share of the top 20 and top 50 groups in 2021 and 2022 is likely to continue in 2023 due in part to the rapid growth of some smaller and medium-sized competitors and in part to the introduction of additional capacity from new sources.
As examples, these new sources include carriers set up by specialist MGAs such as At-Bay, Coalition and Cowbell Cyber, the introduction of MIRIS as a mutual insurer writing cyber risks on behalf of Europe-based owner-member corporates, and the launch of Trium Cyber, writing cyber cover via Lloyd’s syndicate 1322.
With regards to the latter, it may be noted that the Lloyd’s market in aggregate is believed to account for around 20% of global cyber GDPW.
Definition of cyber insurance

Cyber cover is designed to protect organizations and individuals from digital threats such as data breaches, malicious cyber hacks on computer systems or denial-of-service attacks.
This insurance may include first-party cover for the cost of investigating a cybercrime, recovering data lost in a security breach, restoration of computer systems, loss of income incurred by a business shutdown, reputation management, extortion payments demanded by hackers and notification costs, in case of a requirement to notify third parties affected.
It may also include third-party cover for damages, settlements and associated legal costs arising from claims against the policyholder. Moreover, the definition extends to both cyber cover acquired on a stand-alone basis and cover integrated within other types of insurance (e.g. commercial multi-risk).
What does cyber insurance cover?

Cyber insurance is designed to protect businesses against financial losses resulting from cyber incidents. Policies typically provide two types of protection, namely first-party and liability coverage. Here’s what these different types of coverages pay out for.
First-party coverage
This type of coverage pays out for the financial losses the business incurs due to a cyber incident, including the cost of responding to a data breach, restoring and recovering lost or damaged data, lost income resulting from business interruption, ransomware attack payments, and risk assessment of future cyberattacks. Most policies also cover the cost of informing customers about the incident and providing clients with anti-fraud services.
Liability coverage
Also referred to as third-party liability coverage, this provides financial protection against lawsuits filed by third parties, including customers, employees, and vendors, for damages caused by a cyberattack on the business. Policies typically cover court and settlement fees, and regulatory fines.
Methodology and presentation
The ranking of insurer groups by cyber insurance GDPW is based on first-hand guidance from some of the largest underwriters in the sector plus public disclosures (from a small number of them), other public domain sources and Insuramore’s existing rankings of insurer groups worldwide by total P&C and commercial P&C GDPW.
Cyber insurance GDPW for each group are presented as a range of the likely minimum and likely maximum values with the midpoint of the range then used to determine the ranking and approximate global market share.
Edited & Fact checked by 








