Market disruption—fueled by technological change, complex regulations, geopolitical tensions and economic uncertainties—is testing global organizations’ approach to risk and resilience. According to Accenture’s research, most large organizations are transforming faster and more frequently.
By converting cybersecurity from an incident-driven reaction into part of the fabric of transformation efforts, organizations can not only boost cybersecurity resilience, but also position themselves to reinvent the whole enterprise and set a new performance frontier, safely.

The cybersecurity research reveals some organizations are using cybersecurity as a differentiator to deliver better business outcomes (see How to Improve Cybersecurity Protection?).
Annual Accenture’s State of Cybersecurity Resilience research involved 3,000 global respondents from 15 industries across 14 countries.
Those organizations that closely align their cybersecurity programs to business objectives are 18% more likely to increase their ability to drive revenue growth, increase market share and improve customer satisfaction, trust and employee productivity.
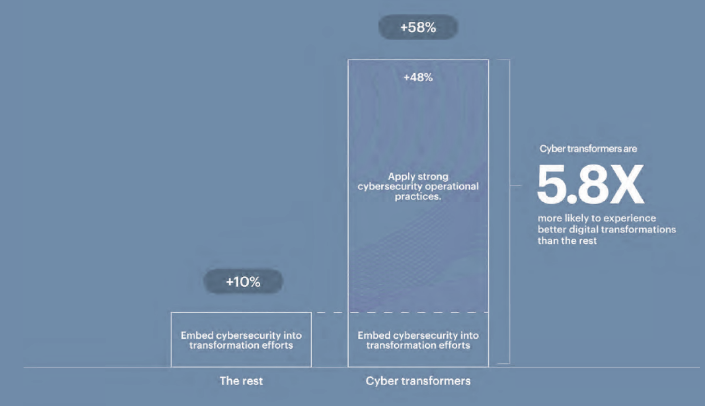
What’s more, organizations that embed key cybersecurity actions into their digital transformation efforts and apply strong cybersecurity operational practices across the organization are nearly six times more likely to experience more effective digital transformations than those that don’t do both.
Cybersecurity as a changemaker
We discovered that the majority of organizations undergoing digital transformation, in our sample, increase their chances of being fully satisfied with the level of cybersecurity embedded in their digital transformation efforts by 10% if they follow three actions.

Recently released Resilience for Reinvention study shows that companies achieving long-term profitable growth display a commitment toward developing a digital core, which consists of three layers: infrastructure and security; data and artificial intelligence (AI); and applications and platforms.
Some organizations— representing 30% of respondents—are already proving how prioritizing cybersecurity makes a difference.
According to Cyber Security Top Trends, organizations have accelerated digital transformation efforts and plan to continue accelerating them as their high-performing cybersecurity actions propel them forward.
Cyber transformers closely align cybersecurity programs to business objectives.
In doing so, they are 18% more likely to increase the following outcomes:
- Their ability to achieve target revenue growth and market share
- Improved customer satisfaction and trust
- Greater employee productivity
Additionally, cyber transformers are nearly twice as good as the rest at involving the cybersecurity team from the start of business planning. And they are far more comfortable with their organization’s internal cybersecurity planning.

Cyber transformers build transformation foundations in two ways
They not only embed three key cybersecurity actions into their transformation efforts, but also establish a better foundation by applying strong cybersecurity operational practices from the start. As a result, they are 5.8X more likely to experience more effective digital transformations than the rest (see How Insurers Can Expand the Cyber Insurance Market?).
What it takes to be a cyber transformer
There are several factors that illustrate the differences between cyber transformers and the rest. 65% of cyber transformers apply three leading practices to excel at risk management. By contrast, just 11% of the rest adopt this “best-in-class” approach (see Future of Global Cyber Insurance Market).
- Integrate cyber risk: A cyber risk-based framework is completely integrated into their enterprise risk management program
- Agree on priorities: Their cybersecurity operations and executive leadership consistently agree on the priority of assets and operations to protect
- Look at risk holistically: They consider cybersecurity risk to a great extent when evaluating overall enterprise risk
Cyber transformers more frequently use cybersecurity-as-a-service to enhance operations.
40% of cyber transformers use third parties or managed services providers to administer cybersecurity operations and address talent shortages, versus 24% of the rest
Based on analysis, cyber transformers performed better than the rest when it comes to taking action to protect their ecosystems.
Cyber transformers are more committed to protecting their ecosystem

For example, cyber transformers more often incorporate their ecosystem or supply chain partners into their incident response plan (45% vs. 37%) and also require them to meet strict cybersecurity standards (41% vs. 29%).
While these ecosystem actions provide cyber transformers with a 10% advantage over the rest, there is room for improvement.
Cyber transformers rely heavily on automation
What’s more, 96% of respondents whose organizations substantially automate their cybersecurity programs recognize that automation helps them alleviate cyber talent shortages, a key challenge for any company seeking cyber resilience.
89% of cyber transformers rely heavily on automation, compared with just 57% of the rest.
As evidence of a man+machine approach becoming more mainstream, Accenture analysis has found that the share of cybersecurity-related AI patents increased 2.7X between January 2017 and October 2022.
In time, generative AI could support enterprise governance and information security, protecting against fraud, improving regulatory compliance, and proactively identifying risk by drawing cross-domain connections and inferences both within and outside the organization.

The revolutionary capabilities of generative AI, which generates new and valuable information, are poised to reshape this industry sector.
Global Generative AI in Insurance Market size will be worth $5,5 bn by 2032 from its current size of $346.3 mn, and growing at a CAGR of 32.9% through the next decade.
The insurance market is undergoing a remarkable transformation, thanks to the exponential growth of generative artificial intelligence (see How AI Technology Can Help Insurers).
Fast-emerging AI developments such as generative AI can drive a new wave of cybersecurity advances.
Indeed, the emergence of ChatGPT has already brought both disruption and opportunity, offering the rapid advancement of cybersecurity capabilities such as threat detection, analysis and response and accelerated use of automation to reduce workload and augment staffing.
Cyber transformers are well placed to execute that reinvention strategy through gains that are a direct result of differentiated cybersecurity practices and behaviors.
And while cybersecurity incidents will still happen every day, on average, cyber transformers report 26% lower cost of breaches and cybersecurity incidents in the past 12 months than the rest—that’s more than a quarter of all costs that could be allocated across the enterprise to optimize operations, fuel growth and improve resilience.
Cyber extra pressure points
While managing secure digital transformation is an important consideration, our research shows there are other ongoing issues that continue to put pressure on all organizations and influence the state of cybersecurity resilience. Looking across our entire set of global respondents, these additional pressure points were revealed.
- An uncertain geopolitical landscape is accelerating threats and attacks. Organizations’ cyber resilience is under pressure from ongoing geopolitical tensions, especially through their supply chains, physical infrastructure and external networks.
- The whole approach to cyber risk is under scrutiny, inside and outside. Organizations are failing to keep pace with the scope and scale of cyber risk.
- There’s still room for improvement in cybersecurity and business alignment. Organizations are better aligning cybersecurity with business leadership, but there are gaps in the effectiveness of their approach.
An uncertain geopolitical landscape is accelerating threats and attacks
Organizations’ cyber resilience is under pressure from ongoing geopolitical tensions, especially through their supply chains, physical infrastructure and external networks, such as investment partners.
The influence of Russia’s aggression in the Ukraine is being felt by almost everyone. Nearly all organizations (97%) have seen an increase in cyber threats since the start of the Russia-Ukraine war and almost all survey respondents have taken some action.
51% of organizations have updated their business continuity and enterprise risk plans and nearly half have increased their incident response capabilities.
At the same time, only 39% of organizations are prioritizing close collaboration with government agencies on policies and recommendations in response to the war. More than half (54%) see third parties and external networks as the most susceptible areas for attack.
Indeed, consistent with last year’s findings, the percentage of successful breaches from outside the organization remains high, even nudging slightly ahead, while for some industries, such as Utilities, supply chain partner threats are higher again at 62%.
The whole approach to cyber risk is under scrutiny, inside and outside
Organizations are failing to keep pace with the scope and scale of cyber risk.
Cyber risk management is challenging inside the organization. Less than half of all survey respondents said that just one aspect of enterprise risk management—their cyber risk-based framework—is completely and accelerating transformation without addressing security along the way can open the door to greater risk.
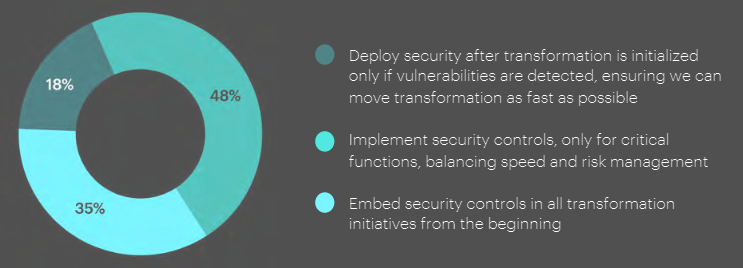
While 35% of respondents said they embed security controls in all transformation initiatives from the beginning, there are still 18% who deploy security after the event.
To transform at speed, security should be baked in, otherwise integrated within the enterprise risk management program.
The regulatory landscape plays a part here, with risk integration leaping to 81% in the highly regulated Banking industry or 65% for the Software and Platforms sector.
The security of digital transformation efforts
Cyber risk is also mounting outside the organization, where cyber threats are increasing due to changes in the threat landscape and cybersecurity omissions leave organizations exposed.
Russia’s invasion of Ukraine spurred reaction from executives to address cybersecurity practices, such as updates to business continuity, incident response and increasing employee cyber awareness.
Indeed, only one-third of all respondents (35%) consider cybersecurity risk “to a great extent” when evaluating overall enterprise risk; this highlights there is still some way to go to make cybersecurity a proactive, strategic necessity within the business.
Improvement in cybersecurity and business alignment
Organizations are better at aligning cybersecurity with business leadership, but there are gaps in the effectiveness of the approach.
Business leaders (CEO and CFO respondents in the research) expect CISOs to go beyond their traditional technical role to act as a representative of the organization.
Business leaders reported the importance of CISOs adopting certain characteristics, such as translating the technical aspects of cybersecurity to the CEO and Board (44%), leading the response during breaches (42%) and establishing trust with customers (41%).
Organizations have a responsibility to define a crisis communications strategy that is agile, that considers the complexities of cyber events and that clearly defines roles and responsibilities for communicating with stakeholders.
How you can employ cybersecurity to drive better results?

From risk assessment and management to security control implementation, and from security awareness and training to incident response and recovery, cybersecurity is essential to maintain dynamic protection in every transformation program.
What’s more, as cyber transformers show, business leaders have an opportunity to make cybersecurity’s impact extend beyond protecting the business in the here and now, to actively influence continuous, dynamic reinvention.
1. Embed cybersecurity to protect the digital core
Security is critical to enabling business agility and scalability as well as driving continued innovation and establishing an organization’s digital core—one that empowers employees and departments to experiment and scale while mitigating risk.
What you can do? Take the three cybersecurity actions and establish a strong foundation with cybersecurity operational practices to improve business outcomes and overall performance.
2. Apply cybersecurity to reconcile digital and physical worlds
Increased access, devices, software and connectivity across the Cloud Continuum and legacy environments has resulted in an ever-expanding threat surface. And while generative AI4 can herald a new era of agility and cyber protection, it also acts as a new threat vector for cyber criminals.
What you can do? Invest in understanding your data, its value and who has access. Re-examine enterprise and customer identity to better bridge the physical and digital worlds. Establish enhanced monitoring and visibility across both legacy and cloud environments using endpoint detection and response (EDR) and security orchestration, automation and response (SOAR) technologies.
3. Make cybersecurity part of the fabric of transformation
The traditional approach to cybersecurity is unsustainable. A global shortage of cybersecurity talent to handle ongoing threats is compounded by fewer people available to handle the effects of cyberattacks on an organization’s business continuity, economics and reputation. The lines are becoming blurred around when transformation begins and ends.
What you can do? Make cybersecurity a cornerstone of your transformation efforts and elevate the CISO reporting so that the function is fundamental to business transformation efforts.
……………….
AUTHORS: Paolo Dal Cin – Lead Accenture Security, Jacky Fox – Senior Managing Director Accenture Security (Europe Lead), Harpreet Sidhu – Senior Managing Director Accenture Security (North America), James Nunn-Price – Senior Managing Director Accenture Security (Growth Markets Lead)








