The impact of current high inflation on German insurance market profitability in 2023 should be limited due to their ability to adjust prices. Europe’s largest economy will likely take a hit from global market conditions in 2023, according to Fitch Ratings.
However, the anticipated recession may decrease the demand for private insurance products.
German Non-Life Insurance

The German non-life insurance market is likely to experience a difficult financial year in 2023 due to several macroeconomic factors, such as the current inflation trend that has hit markets across the continent. This reflecting expectation that inflationary pressure on property and liability claims will overweigh higher fixed-income investment yields.
Reinvestment yields are likely to exceed maturing fixed-income investment coupons until 2024 and we expect return rates to increase to 2.8% for 2023 and 3% for 2024.
Increasing investment income helps insurers to mitigate the negative impact from claims inflation, but we believe that the additional investment income will be smaller than the decline in underwriting income.
A sustainable investment income increases compensation for the lower underwriting profitability and would support a revision of the sector outlook to stable.
Germany has been one of the countries most affected by the energy crisis this winter, which could hit its economy further. Economic factors for the continent’s economic powerhouse seem mixed too.
The country’s unemployment rate is at 3.1%, expected to hit 3.5% in 2023, with inflation at 8.8% and expected to fall but stay high at 7.5% in 2023.
GDP growth in 2023 will contract – with a 0.6% fall. “Higher building and borrowing costs are expected to weigh on construction,” said the EU’s office of the Directorate-General for Economic and Financial Affairs report on its economy. The gradual adjustment of supply chains and overall solid corporate finances should set the stage for a resumption of investment growth in the course of 2023.
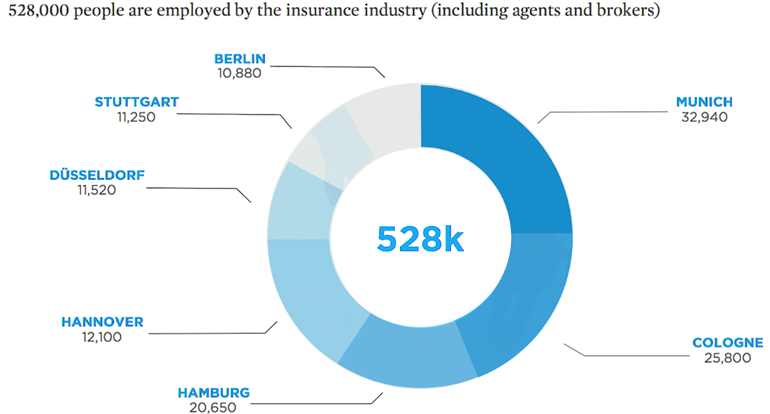
German insurance market overview
While production of equipment was still increasing, energy intensive intermediate industries were cutting output. Investment dynamics were generally wavering.
Investment income is also likely to be reduced by negative credit migration. Underwriting profitability to deteriorate in 2022 and 2023 despite multi-decade high natural catastrophe losses for the sector.
Large 2021 catastrophe net losses were largely offset by a pandemic-related reduction in claims frequency in 1H21 (see Global Natural Catastrophe & Hazard Review). A sector combined ratio of 98% for 2023, relative to our 96% estimate for 2022 (2021: 94%).
In absolute terms, insurers’ net underwriting result to deteriorate to EUR1.5 billion in 2023 from an estimated EUR2.7 billion in 2022 (2021: EUR3.9 billion), before the change in the claims equalisation reserve.
Rates in buildings, property and motor lines will continue to increase in 2023, albeit not sufficiently to cover the rise in claims from claims inflation.
German non-life market to achieve premium growth of 6% in 2023, up from an estimated 5% in 2022 (2021: 4.6%), due to rate increases in commercial insurance, buildings and motor insurance.
Commercial and buildings insurance to report annual premiums growth of at least 6% until 2024. If premium growth would strongly outperform our expectations, the sector outlook could be revised to ‘neutral’.
Prerequisite would be that embedded rate rises are sufficient to compensate for the negative impact from claims inflation.
German life insurance sector

The neutral outlook for the German life insurance sector reflects expectation of a mixed operating environment, with improving investment yields and strong capital positions, but also declining new business and a generally uncertain investment environment.
The increase in market interest rates over the past year generally improves the situation by lowering the reinvestment risk for German life companies, but the volatility in fixed-income and equity markets has risen, making it more difficult to make investment decisions.
The strong increase in consumer inflation reduces consumers’ available incomes and we therefore expect it to dampen demand for life insurance products in 2023.
In absolute terms, insurers’ net underwriting result to deteriorate to EUR1.5 billion in 2023 from an estimated EUR2.7 billion in 2022 (2021: EUR3.9 billion), before the change in the claims equalisation reserve.
Rates in buildings, property and motor lines will continue to increase in 2023, albeit not sufficiently to cover the rise in claims driven by claims inflation.
Positive factors are insurers’ diverse business mix, significant earnings from sources that are not interest sensitive, and strong capital positions.
The average Solvency II (S2) coverage ratio, excluding transitional measures on technical provisions, to increase in 2022, from 262% at end-2021, driven by a further rises in market interest rates.
The rise in market interest rates brings fixed-income reinvestment yields now close to the effective guarantees of the business in force portfolio, which considerably reduces reinvestment risks.
Health Insurance Performs Strongly

The health insurance sector’s profitability declined in 2022, despite starting from a strong position. Claims growth rose by 4%, following two years of low rises due to the pandemic.
Along with slower premium growth in 2022, caused by a decrease in the discount rate used to calculate long-term reserves, this has led to an increase in the combined ratio.
The average ratio to remain comfortably under 90% in 2022-2023. The rise in market interest rates has relieved pressure on health insurers, who no longer need to make large price adjustments to compensate for the declining discount rate.
Premium growth in 2023 to remain moderate at about 3% despite inflation-driven price rises.
In outlook report, Fitch forecast a recession in the country in 2023. This may result in lower demand for both full coverage and supplementary products, as economic uncertainties may make individuals hesitant to switch to full-coverage private health insurance.
It may also decrease demand for company health insurance, the sector’s fastest-growing product.
Private Health Insurance Sector Continues to Perform
The effect of the current high inflation rate on the German private health insurance sector’s profitability to be limited due to its ability to make price adjustment although a weak German economy could reduce policyholder growth prospects.
The profitability in the health sector to have deteriorated in 2022, albeit from a strong level.
Analytics expect that claim growth returned to the long-term average of about 4%, following two years of pandemic-related growth of about 2%.
Premium growth slowed to 3.1% from 5.8% in 2021 and 4.5% in 2020 due to an increase in the discount rate used to calculate the long-term reserves, which followed the rising market interest rate. These effects will lead to higher combined ratios in 2022.
The profitability in the private health sector will remain very strong with an average combined ratio of comfortably under 90%.
High overall inflation rate to have a significant impact on German private health insurers’ profitability.
The overall healthcare expenses to increase, for example, due to the increasing wages or higher energy costs, private health insurers should be able to adjust their prices to cover this.
Germany Motor Insurance Market
The impact of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic is expected to result in a non-life re/insurance market loss of between EUR 1.25 billion to EUR 1.75 billion (USD 1.47 billion – USD 2.1 billion) in Germany, influenced mostly by nationwide business closures.
German insurers are often globally positioned, which reduces susceptibility to weak results in the domestic market. The estimated revenue of the industry was EUR 2.2 billion.
Some form of car insurance must cover all drivers, and people cannot register a vehicle without it. If a person is a long-term resident of Germany, they need German car insurance. Foreign car insurance is not enough even if they have brought a car from abroad to Germany.
The German motor insurance market is segmented by type (third-party, partial coverage, and comprehensive) and by distribution channel (brokers, agency, direct, banks, and others)
Digitalization is a central concern of the insurance industry. Many insurance companies are modernizing their IT infrastructures, moving to cloud solutions or investing in new technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) or blockchain to provide enhanced products and services to their customers.
German insurers spent USD 416.77 million in total on IT. One of the key investment priorities in insurance companies includes the optimization of business processes, the operating organization, and the insurance IT. This weighting has increased further by the momentum of Digitization and its dynamic effects on competitiveness.
…………………
AUTHORS: Mahsa Delgoshaei – Director Fitch Ratings, Dr Stephan Kalb – Senior Director Fitch Ratings








